
Before you begin
- Labs create a Google Cloud project and resources for a fixed time
- Labs have a time limit and no pause feature. If you end the lab, you'll have to restart from the beginning.
- On the top left of your screen, click Start lab to begin
If you are new to cloud computing or looking for an overview of Google Cloud and Firebase, you are in the right place. Read on to learn about the specifics of this lab and areas that you will get hands-on practice with.
In this lab, you will learn about the following:
This is an introductory-level lab and the first lab you should take if you're unfamiliar with Firebase. If you are already experienced with Firebase Cloud console, consider taking one of the following labs:
If you decide to take one, be sure to end this lab now.
If you have a personal or corporate Google Cloud account or project, sign out of that account. If you stay logged in to your personal/corporate account and run the lab in the same browser, your credentials could get confused, resulting in getting logged out of the lab accidentally.
If you use ChromeOS, please run your lab using an Incognito window.
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources are made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a dialog opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details pane with the following:
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
Click Activate Cloud Shell 
Click through the following windows:
When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your Project_ID,
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
Output:
Output:
gcloud, in Google Cloud, refer to the gcloud CLI overview guide.
Certain Compute Engine resources live in regions or zones. A region is a specific geographical location where you can run your resources. Each region has one or more zones. For example, the us-central1 region denotes a region in the Central United States that has zones us-central1-a, us-central1-b, us-central1-c, and us-central1-f.
| Regions | Zones |
|---|---|
| Western US | us-west1-a, us-west1-b |
| Central US | us-central1-a, us-central1-b, us-central1-d, us-central1-f |
| Eastern US | us-east1-b, us-east1-c, us-east1-d |
| Western Europe | europe-west1-b, europe-west1-c, europe-west1-d |
| Eastern Asia | asia-east1-a, asia-east1-b, asia-east1-c |
Resources that live in a zone are referred to as zonal resources. Virtual machine Instances and persistent disks live in a zone. To attach a persistent disk to a virtual machine instance, both resources must be in the same zone. Similarly, if you want to assign a static IP address to an instance, the instance must be in the same region as the static IP.
The Firebase suite of tools is linked to a Google Cloud project, so you will see a project identifier and project name in the Firebase information.
Firebase projects are accessed via the Firebase console. Take a moment to open the Firebase console in a new Incognito window.
The first step to access a Firebase project is to select or create a project. Firebase provides a demo project for users to experience the environment.
In the Firebase user interface, the project Overview->Project Settings
settings menu option will display information about the project. The upper-left corner of the central pane contains a card labeled Project General that looks like this:
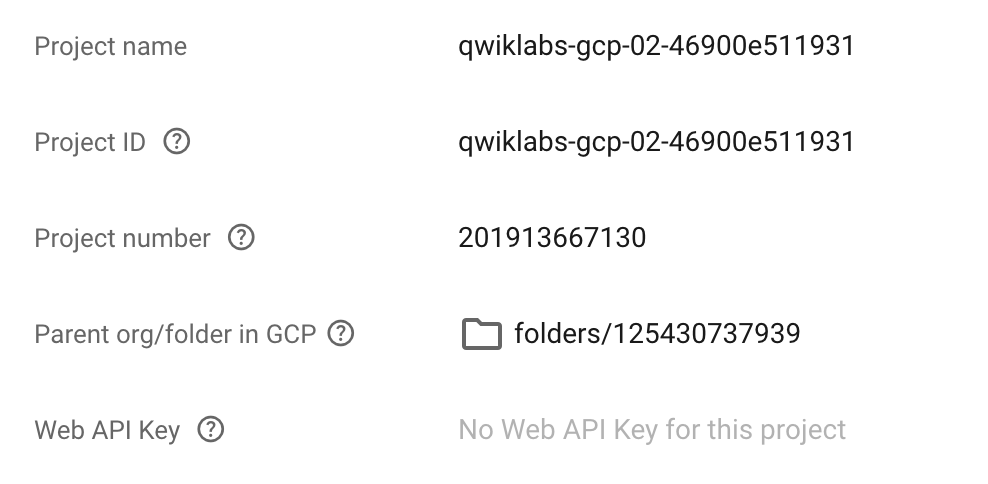
A Firebase Project has a name, number, and ID. These identifiers are frequently used when interacting with Google Cloud services. You are working with one project to get experience with a specific service or feature of Firebase.
From the project setting page, you will also see any apps that have been registered under the current project.
Firebase includes support for a number of different language runtimes including:
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
Clicking the Navigation menu icons provides quick access to Firebase's core services.
Firebase Authentication provides backend services, easy-to-use SDKs, and ready-made UI libraries to authenticate users to your app. It supports authentication using passwords, phone numbers, popular federated identity providers like Google, Facebook and Twitter, and more.
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
Firebase Hosting is production-grade web content hosting for developers. With a single command, you can quickly deploy web apps and serve both static and dynamic content to a global CDN (content delivery network). You can also pair Firebase Hosting with Cloud Functions or Cloud Run to build and host microservices on Firebase.
Firebase Hosting can be used to deploy static and dynamic web content. It provides a global CDN distribution, automatic SSL certificates, and custom domain support.
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
Cloud Storage for Firebase is a powerful, simple, and cost-effective object storage service built for Google scale. The Firebase SDKs for Cloud Storage add Google security to file uploads and downloads for your Firebase apps, regardless of network quality.
Firebase Storage is a scalable, durable, and highly available object storage service for storing user-generated content. It is a great way to store images, videos, audio files, and other types of files in the cloud.
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
Cloud Firestore is a flexible, scalable database for mobile, web, and server development from Firebase and Google Cloud. Firebase Cloud Firestore is a NoSQL document database. This means your data is stored in documents organized in collections. Documents can contain a variety of data types, including strings, numbers, arrays, objects, and geopoints. Like Firebase Realtime Database, it keeps your data in sync across client apps through real time listeners and offers offline support for mobile and web so you can build responsive apps that work regardless of network latency or Internet connectivity. Cloud Firestore also offers seamless integration with other Firebase and Google Cloud products, including Cloud Functions.
Firebase Cloud Firestore provides eventual consistency by default. This means that your data may not be immediately available to all clients after it is written. However, you can use transactions to ensure your data is always consistent.
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
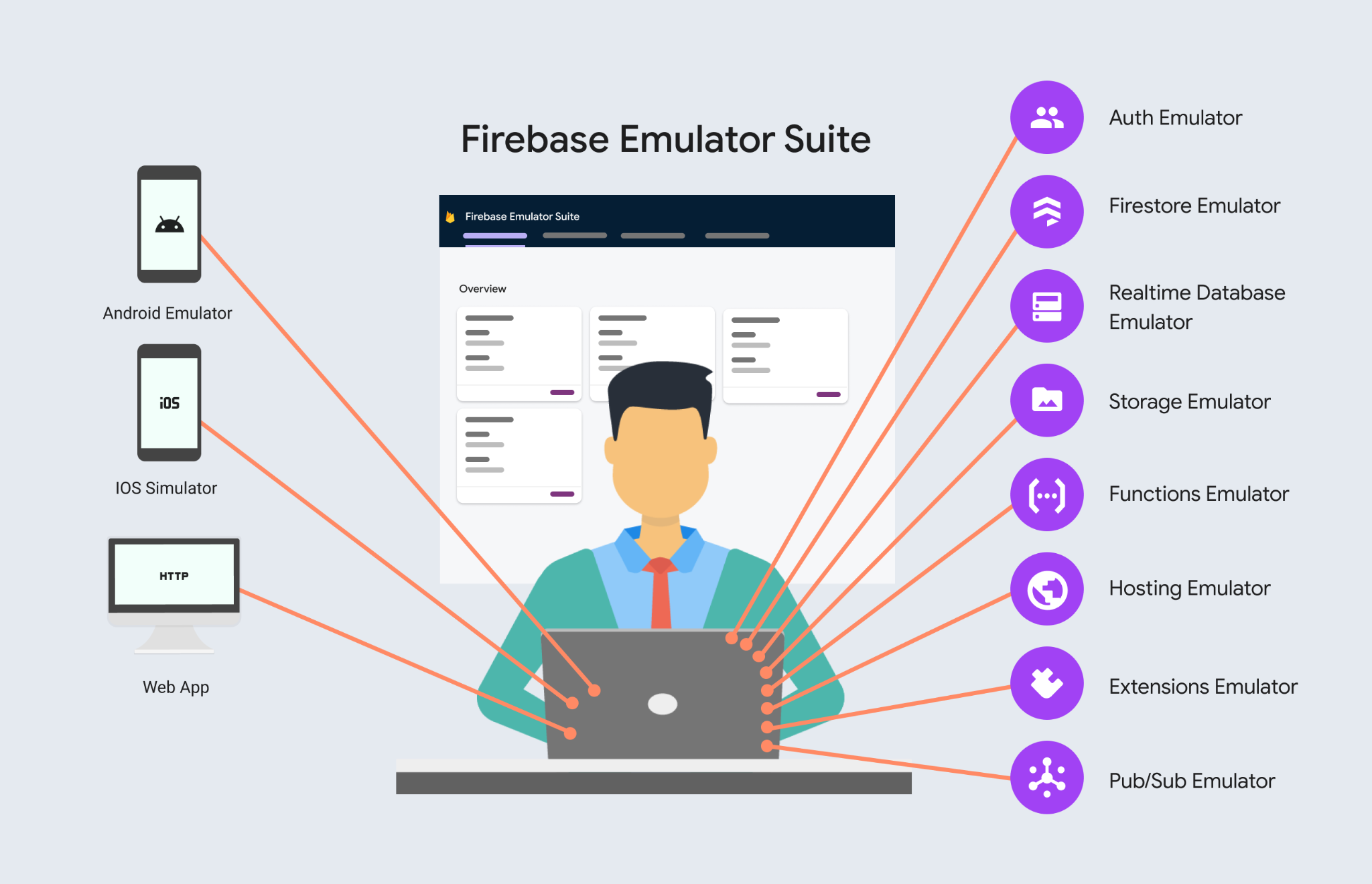
The Emulator Suite consists of Firebase service emulators built to accurately mimic the behavior of Firebase services. This means you can connect your app directly to these emulators to perform integration testing or QA without touching production data.
For example, you could connect your app to the Cloud Firestore emulator to safely read and write documents in testing. These writes may trigger functions in the Cloud Functions emulator. However your app will still continue to communicate with production Firebase services when emulators are not available or configured.
Answer the following multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of the concepts covered so far.
When you have completed your lab, click End Lab. Your account and the resources you've used are removed from the lab platform.
You will be given an opportunity to rate the lab experience. Select the applicable number of stars, type a comment, and then click Submit.
The number of stars indicates the following:
You can close the dialog box if you don't want to provide feedback.
For feedback, suggestions, or corrections, please use the Support tab.
In just 30 minutes, you developed a solid understanding of the Cloud console and the platform's key features. You learned about projects, roles, and the types of services the platform offers. You also practiced with Cloud IAM and the API libraries. You are now ready to take more labs.
Continue your quest with Getting started with Webpack, or check out these other Google Cloud Skills Boost labs:
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated November 4, 2024
Lab Last Tested November 4, 2024
Copyright 2025 Google LLC. All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




This content is not currently available
We will notify you via email when it becomes available

Great!
We will contact you via email if it becomes available


One lab at a time
Confirm to end all existing labs and start this one
