
Before you begin
- Labs create a Google Cloud project and resources for a fixed time
- Labs have a time limit and no pause feature. If you end the lab, you'll have to restart from the beginning.
- On the top left of your screen, click Start lab to begin
Outbound connectivity
/ 33
Inbound connectivity
/ 33
East-west segmentation
/ 34
This lab was developed with our partner, Fortinet. Your personal information may be shared with Fortinet, the lab sponsor, if you have opted in to receive product updates, announcements, and offers in your Account Profile.
This lab is intended for network administrators implementing network traffic inspection in Google Cloud using FortiGate next-gen firewalls. You will learn the reference HA architecture and configure inbound, outbound and east-west traffic inspection using a FortiGate next-gen firewall cluster.
Using FortiGates in public cloud helps to protect cloud resources against intrusion, detect compromised hosts, and increases visibility of network traffic.
In this lab you learn how to:
The lab starts with all cloud resources pre-deployed to match the FortiGate recommended architecture described below. Although all cloud resources are deployed and do not require any additional configuration, the FortiGates have only the following elements configured:
and require additional configuration necessary to provide the desired functionality.
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
Click Next.
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
Click Next.
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

FortiGate reference architecture for Google Cloud leverages 2 common "building blocks": active-passive HA cluster in load balancer sandwich, and hub-and-spoke with VPC peering and custom route export.
High availability clusters are deployed between 2 separate availability zones of the same region to elevate the SLA of the solution to 99.99%. FortiGates are usually deployed in an active-passive pair leveraging Fortinet's proprietary FGCP protocol for configuration and state synchronization. Traffic from the Internet is directed to the currently active VM instance using an external load balancer to be matched against access policy, inspected against malicious payload and redirected using a Virtual IP to the destination server (in case of this lab - frontend VM). Packets from VPC Network is routed to FortiGates using internal load balancer as the next hop.
While the VPC Peering itself is non-transitive (two VPC networks can communicate only if directly peered), it's different if peering is combined with custom route and a routing NVA (network virtual appliance). A custom route created in the hub VPC with next hop set to FortiGate (or ILB fronting a FortiGate cluster) can be exported to all peered VPCs using export custom route property. The route imported to peered spoke VPCs will apply to all traffic leaving the spoke VPC sending it to the FortiGate appliance. Note that the route table is evaluated only once when the packet is leaving its source, it is not re-evaluated once the packet crosses the peering (so it's not affected by a peered subnet route in the hub VPC when on the way to FortiGate). It is important to note that the default route in spoke VPCs would take precedence over the route imported via the peering and thus has to be deleted.
This lab's resources (VM instances and VPC networks) are distributed across two Google Cloud projects - IDs of both will be listed on the left once the lab starts and provisions. You might find it convenient to open two consoles - one for each project. You can use the provided buttons to do so.
FortiGate virtual appliances can be managed using the web GUI available over HTTPS protocol on the default port, or using the command line interface, in the GUI or via SSH. Configuration of the FortiGate HA cluster is managed only using the primary (active) instance and automatically replicated to the secondary (passive) instance. The secondary instance management console can be optionally accessed using its public IP address to verify clustering and replication statuses.
While the cloud network infrastructure is pre-configured for this lab, you still need to adjust FortiGates routing configuration to indicate the route to workload VPCs (frontend and backend):
If it's not clear for you what the "workload subnets" are and what are their addresses go back to the Overview > Architecture section.
Workload servers are already deployed, but they cannot finish their bootstrapping without connectivity with Internet. In this step you enable and inspect outbound traffic from workload VMs in peered networks to Internet.
Go to the Workloads Cloud console. Make sure you are in the
Use the Navigation Menu to the left to get to Compute Engine and look at the instances. Stop and start frontend-vm and backend-vm instances using STOP and START/RESUME buttons at the top of the instance details page in Cloud console
In this step you enable access from Internet to a web application frontend VM via FortiGate. In production environment you use a farm of compute resources (VMs or serverless) behind an internal load balancer. For the sake of simplicity this lab uses two standalone VMs to emulate frontend and backend farms.
In a cloud environment protected by a firewall no other VM is directly available from Internet. You can enforce this policy using Organization Policy constraints constraints/compute.vmExternalIpAccess, but using constraints is beyond the scope of this lab.
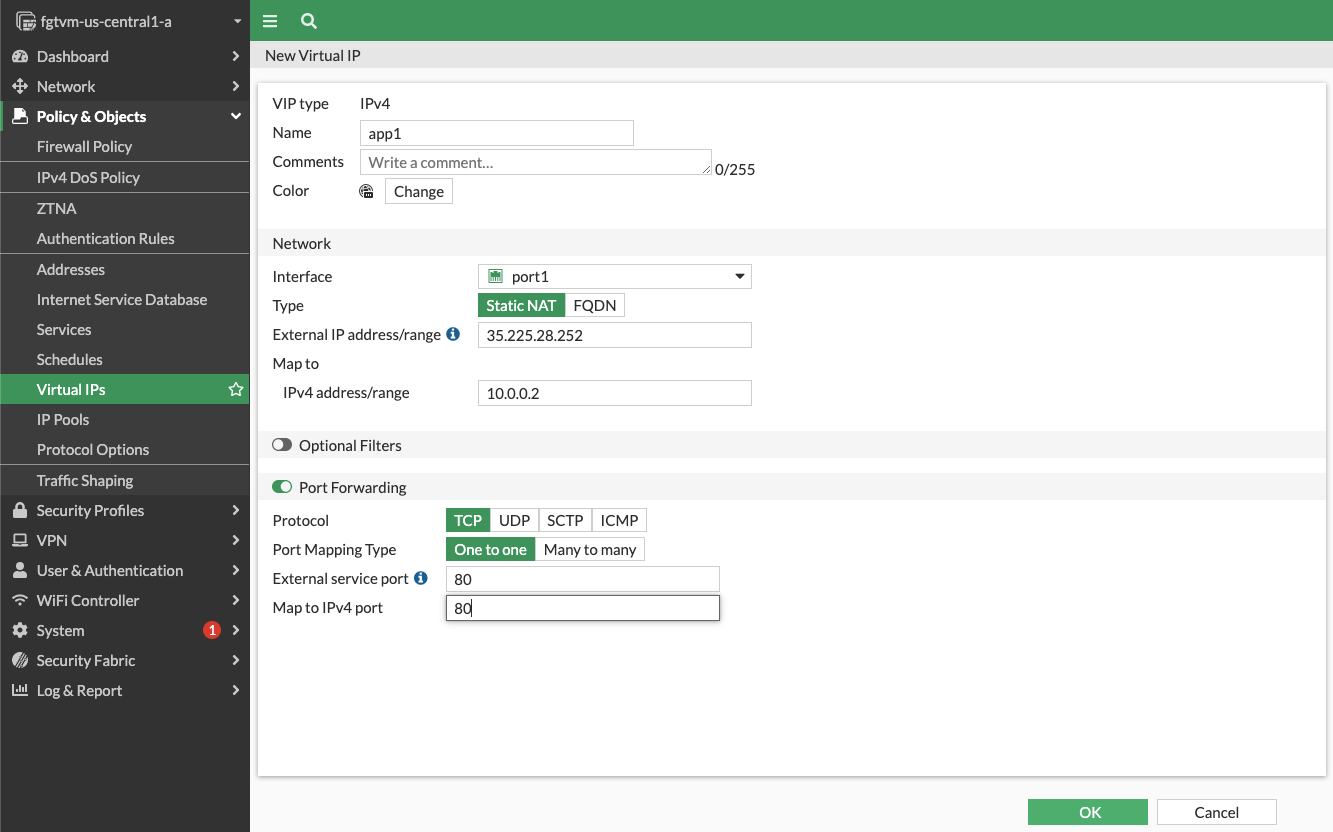
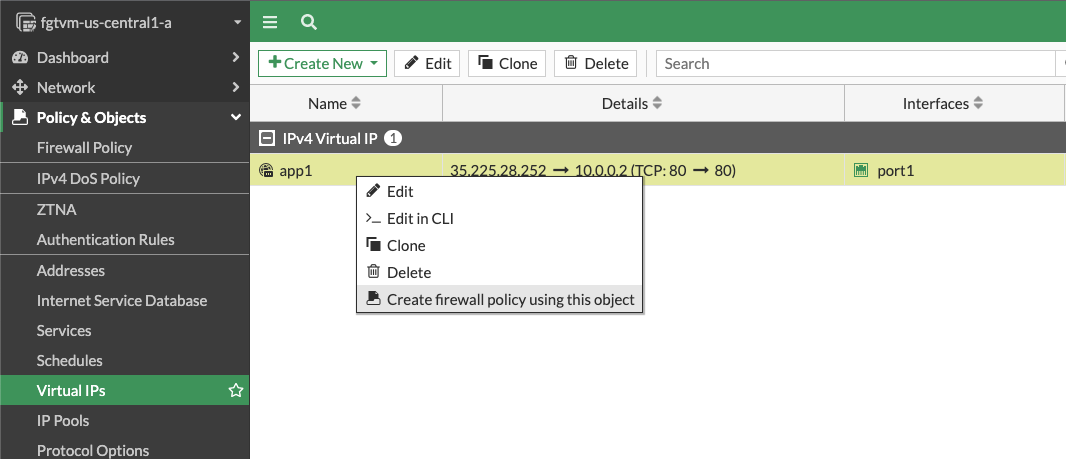
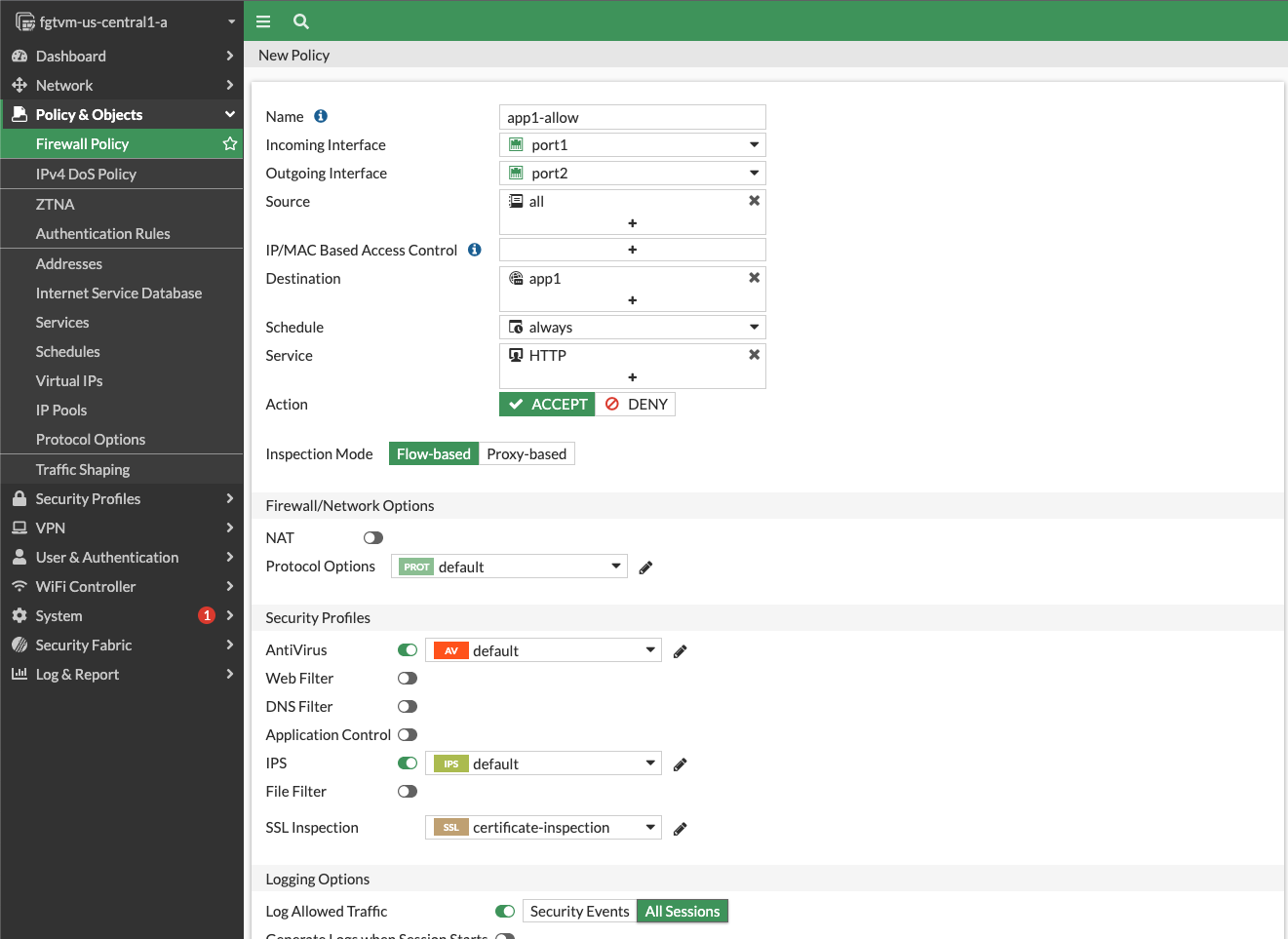
Some applications might require traffic inspection between application tiers (eg. using IPS - Intrusion Prevention System). Note that in Google Cloud you must deploy different application tiers into different VPC networks. Due to the nature of Google Cloud networking only traffic leaving a VPC can be redirected to a network virtual appliance for inspection.
In this step you enable secure connectivity between VMs in frontend and backend VPC networks. You use Fortinet Fabric Connector to build a firewall rule based on metadata rather than using static CIDRs.
Connect to primary FortiGate
Use left menu to navigate to Policy & Objects > Addresses and create dynamic addresses for frontend and backend network tags:
Repeat steps above to create a new address for the backend network tag
Create a firewall policy allowing traffic from frontend to backend with port2 as both source and destination interface
Use your web browser to connect to ELB public IP address over HTTP protocol. You should receive a It works! message (if you see the default nginx page or 502 error - wait few seconds and refresh the page).
Click Try getting EICAR button to attempt downloading a harmless EICAR test virus file. Your attempt will be blocked by FortiGate. You can verify details about detected incident in FortiGate Forward Traffic log.
You completed this lab and learned how to use FortiGate to protect inbound and outbound traffic between the Internet and Google Cloud as well as inspect traffic between VMs in different VPC Networks. Click the End Lab button at the top left to close the lab.
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated: November 14, 2024
Lab Last Tested: November 14, 2024
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




This content is not currently available
We will notify you via email when it becomes available

Great!
We will contact you via email if it becomes available


One lab at a time
Confirm to end all existing labs and start this one
