Scaling Microservices Applications: Migration to Redis Enterprise on Google Cloud
- GSP1177
- Overview
- Setup and Requirements
- Task 1. Use Terraform to provision the infrastructure components and deploy the eCommerce website application
- Task 2. Migrate the shopping cart data from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise using RIOT, Redis Input and Output Tool
- Task 3. Roll back to the OSS Redis to back the shopping cart content
- Task 4. Patch the "Cart" deployment to point to the Redis Enterprise Database again for production
- Congratulations!
- Cleaning up
This lab was developed with our partner, Redis. Your personal information may be shared with Redis, the lab sponsor, if you have opted in to receive product updates, announcements, and offers in your Account Profile.
GSP1177
Overview
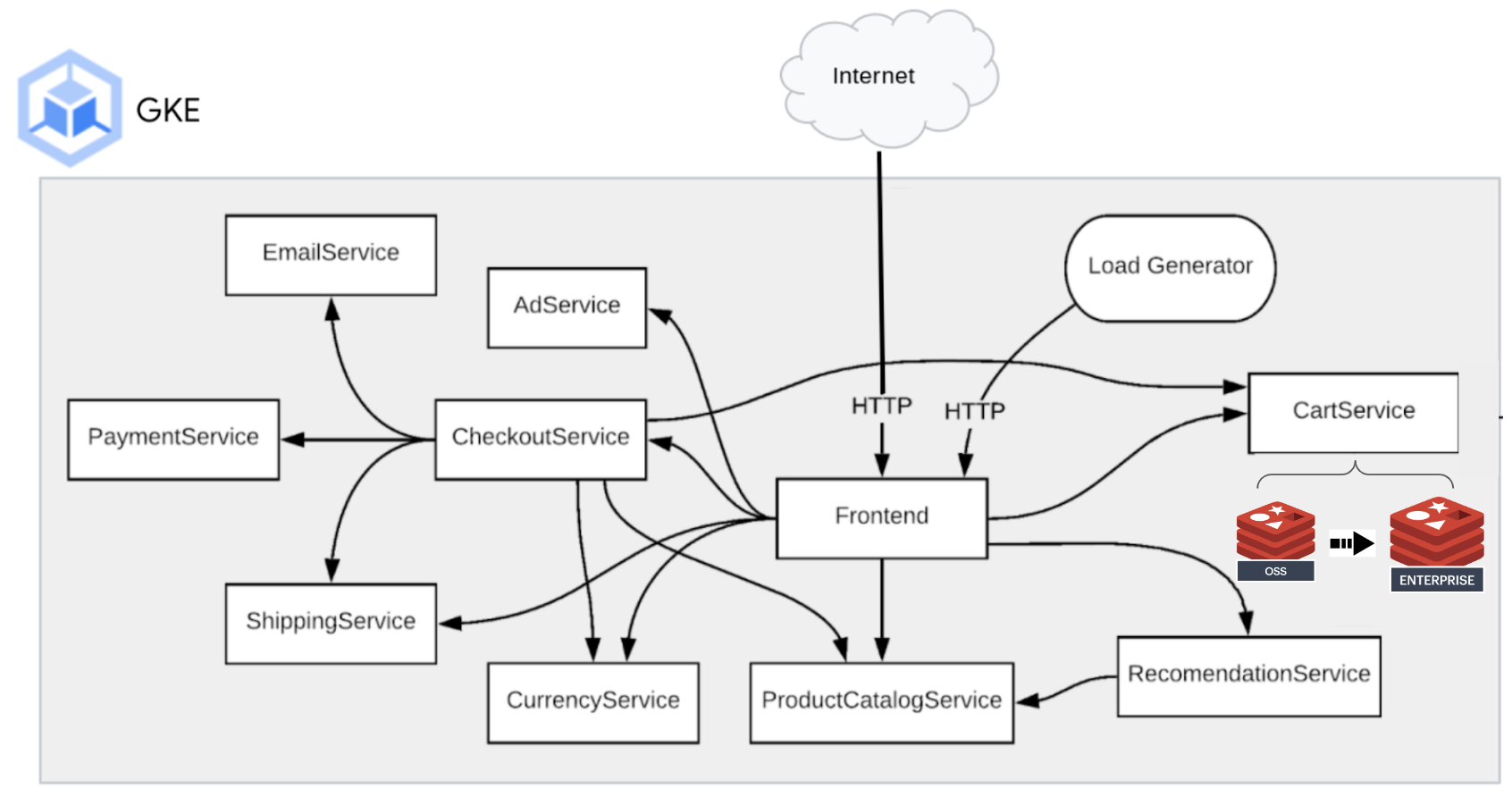
In this lab, you will deploy a fully functioning microservices e-Commerce website application on Google Cloud using Redis to run the shopping cart service. Open Source Redis is the original database to run the shopping cart service. It will migrate the shopping cart data to Redis Enterprise for scalability and high availability with minimal downtime.
Objectives
In this lab, you will learn how to:
-
Use Terraform to provision the following components in this order:
- VPC Network
- Google Kubernetes Engine cluster
- Deploy e-Commerce microservices application
- Deploy Redis Enterprise Cluster and Database using Redis Enterprise Operator for Kubernetes
-
Migrate the shopping cart data from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise using RIOT ( Redis Input and Output Tool)
-
Roll back to the OSS Redis to back the shopping cart content
-
Patch the "Cart" deployment to point to the Redis Enterprise Database again for production
Setup and Requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account. -
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}} You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}} You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials. Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges. -
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

Activate Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
- Click Activate Cloud Shell
at the top of the Google Cloud console.
When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your Project_ID,
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- (Optional) You can list the active account name with this command:
- Click Authorize.
Output:
- (Optional) You can list the project ID with this command:
Output:
gcloud, in Google Cloud, refer to the gcloud CLI overview guide.
Task 1. Use Terraform to provision the infrastructure components and deploy the eCommerce website application
- In Cloud Shell, clone the following Github repository for the lab:
- Create your own terraform.tfvars. Copy this code and run it on Cloud Shell:
- Initialize Terraform:
- Deploy the stack:
On success, you will see similar output below:
- Store Redis Enterprise database information in environment variables for later use:
- Target your environment to the GKE cluster:
- Get the External-IP from the web application (in the redis namespace)
-
Access the eCommerce website application by pointing your browser with the IP address from the following command as http://<EXTERNAL-IP>
-
The web application is using the inbuilt OSS Redis container as the backing store for the shopping cart by default. Make sure you add some items to your shopping cart in order to see that data migration from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise works later in the lab.
Task 2. Migrate the shopping cart data from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise using RIOT, Redis Input and Output Tool
- Set to redis namespace:
- Show the current pointer for the cartservice (it'll show it pointing to OSS Redis)
- Create a Kubernetes secret for the Redis Enterprise database connection:
- Run a Kubernetes job to migrate data from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise database (should take about 15 seconds or so):
- Show the current pointer for the cartservice
Run a Kubernetes patch command below to update the cartservice deployment to point to the new Redis Enterprise database endpoint (should take about 30 seconds):
- Apply Kubernetes patch command to the cartservice
- Show the new pointer for the cartservice (it'll show it pointing to OSS Redis)
- Verify if the same items remain in the shopping cart are now backed by the Redis Enterprise database by refreshing your browser and accessing the shopping cart content again. The same items should appear in the shopping cart. Then add a few items to the shopping cart in order to verify the online boutique web application is successfully pointing to the Redis Enterprise database.
Task 3. Roll back to the OSS Redis to back the shopping cart content
- Run the following patch command to configure the shopping cart to use OSS Redis again (Should take about 30 seconds):
- Verify that the service has been pointed to the OSS Redis instance
- Refresh your browser and access the shopping cart content. You should not see the new items which are added earlier when Redis Enterprise is backing the shopping cart content. It is because the new items added to the shopping cart backed by the Redis Enterprise database is not replicated to the Redis OSS instance.
Task 4. Patch the "Cart" deployment to point to the Redis Enterprise Database again for production
- Run a K8s patch command to update the cartservice deployment to point to the Redis Enterprise Endpoint (Should take about 30 seconds):
- Verify that the service has been pointed to the Redis Enterprise
- Refresh your browser and access the shopping cart content. You should see the items which are added earlier. Now that everything is working and your items are still in your cart, you can delete the OSS Redis deployment as follows:
Hooray!!! We are now ready for the upcoming big customer sales events.
Congratulations!
To summarize, you have accomplished the following in the lab:
- Use Terraform to provision the following components in this order:
- VPC Network
- Google Kubernetes Engine cluster
- Deploy e-Commerce microservices application
- Deploy Redis Enterprise Cluster and Database using Redis Enterprise Operator for Kubernetes
- Migrate the shopping cart data from OSS Redis to Redis Enterprise using RIOT ( Redis Input and Output Tool)
- Roll back to the OSS Redis to back the shopping cart content
- Patch the "Cart" deployment to point to the Redis Enterprise Database again for production
Next steps / Learn more
- Learn more about RIOT for data migration between Redis instances
- Redis Enterprise on the Google Cloud Marketplace
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Cleaning up
The resources will be cleaned up when the Lab is stopped or the session expired, please click the "End Lab" button to terminate the lab if you complete the session earlier than the clock.
Manual Last Updated: December 27, 2023
Lab Last Tested: November 22, 2023
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
