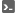SCBL007
개요
이 실습에서는 Spanner 데이터베이스를 활용하는 애플리케이션을 작성하고 Cloud Run Functions와 Cloud Run 모두에 배포합니다. 또한 개발 환경에서 사용할 Spanner 에뮬레이터를 설치하고 구성한 후 사용 설정합니다.
목표
이 실습에서는 다음을 수행하는 방법에 대해 알아봅니다.
- Spanner 데이터베이스에 읽기와 쓰기를 수행하는 Cloud Run Functions를 배포합니다.
- 개발을 위한 Spanner 에뮬레이터를 설정하고 사용합니다.
- Spanner 데이터를 읽고 쓰는 데 사용할 REST API를 빌드합니다.
- REST API를 Google Cloud Run에 배포합니다.
설정 및 요구사항
실습 시작 버튼을 클릭하기 전에
다음 안내를 확인하세요. 실습에는 시간 제한이 있으며 일시중지할 수 없습니다. 실습 시작을 클릭하면 타이머가 시작됩니다. 이 타이머는 Google Cloud 리소스를 사용할 수 있는 시간이 얼마나 남았는지를 표시합니다.
실무형 실습을 통해 시뮬레이션이나 데모 환경이 아닌 실제 클라우드 환경에서 직접 실습 활동을 진행할 수 있습니다. 실습 시간 동안 Google Cloud에 로그인하고 액세스하는 데 사용할 수 있는 새로운 임시 사용자 인증 정보가 제공됩니다.
이 실습을 완료하려면 다음을 준비해야 합니다.
- 표준 인터넷 브라우저 액세스 권한(Chrome 브라우저 권장)
참고: 이 실습을 실행하려면 시크릿 모드 또는 시크릿 브라우저 창을 사용하세요. 개인 계정과 학습자 계정 간의 충돌로 개인 계정에 추가 요금이 발생하는 일을 방지해 줍니다.
- 실습을 완료하기에 충분한 시간. 실습을 시작하고 나면 일시중지할 수 없습니다.
참고: 계정에 추가 요금이 발생하지 않도록 하려면 개인용 Google Cloud 계정이나 프로젝트가 이미 있어도 이 실습에서는 사용하지 마세요.
Google Cloud Shell 활성화하기
Google Cloud Shell은 다양한 개발 도구가 탑재된 가상 머신으로, 5GB의 영구 홈 디렉토리를 제공하며 Google Cloud에서 실행됩니다.
Google Cloud Shell을 사용하면 명령줄을 통해 GCP 리소스에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
-
GCP Console의 오른쪽 상단 툴바에서 Cloud Shell 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다.
-
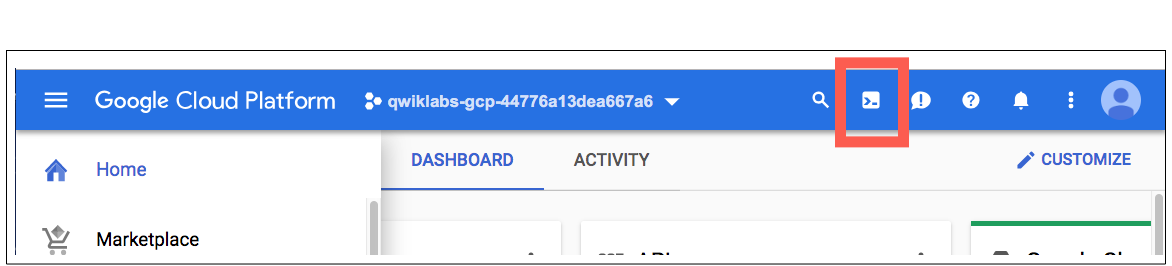
( 계속) Continue을 클릭하십시오.
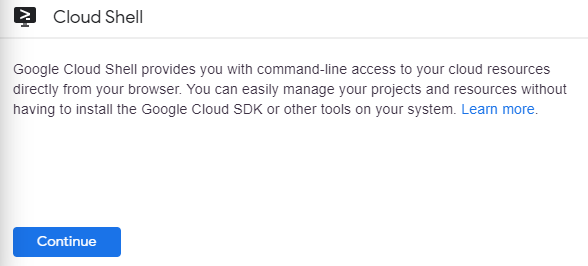
환경을 프로비저닝하고 연결하는 데 약간의 시간이 걸립니다. 연결되면 이미 인증되었으며 프로젝트는 PROJECT_ID 로 설정됩니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다.
gcloud는 Google Cloud Platform의 명령줄 도구입니다. Cloud Shell에 사전 설치되어 있으며 탭 자동 완성을 지원합니다.
다음 명령어로 사용 중인 계정 이름 목록을 표시할 수 있습니다.
gcloud auth list
출력:
Credentialed accounts:
- <myaccount>@<mydomain>.com (active)
출력 예:
Credentialed accounts:
- google1623327_student@qwiklabs.net
다음 명령어로 프로젝트 ID 목록을 표시할 수 있습니다.
gcloud config list project
출력:
[core]
project = <project_ID>
출력 예:
[core]
project = qwiklabs-gcp-44776a13dea667a6
작업 1. 테스트 데이터가 포함된 데이터베이스 만들기
-
Google Cloud 콘솔 제목 표시줄에서 Cloud Shell 활성화( )를 클릭합니다. 메시지가 표시되면 계속을 클릭합니다. 또는 Cloud 콘솔 창을 선택한 다음 키보드로 G 키와 S 키를 차례로 입력하여 동일한 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
)를 클릭합니다. 메시지가 표시되면 계속을 클릭합니다. 또는 Cloud 콘솔 창을 선택한 다음 키보드로 G 키와 S 키를 차례로 입력하여 동일한 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다.
-
다음 명령어를 실행하여 Cloud Build, Cloud Run, Eventarc API를 사용 설정합니다. 명령어를 승인하라는 메시지가 표시되면 이를 수행합니다.
gcloud services enable cloudbuild.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable eventarc.googleapis.com
- 다음 Bash 명령어를 실행하여 Pets 데이터베이스의 스키마 파일을 만듭니다.
mkdir ~/lab-files
cd ~/lab-files
cat > ./pets-db-schema.sql << ENDOFFILE
CREATE TABLE Owners (
OwnerID STRING(36) NOT NULL,
OwnerName STRING(MAX) NOT NULL
) PRIMARY KEY (OwnerID);
CREATE TABLE Pets (
OwnerID STRING(36) NOT NULL,
PetID STRING(MAX) NOT NULL,
PetType STRING(MAX) NOT NULL,
PetName STRING(MAX) NOT NULL,
Breed STRING(MAX) NOT NULL,
) PRIMARY KEY (OwnerID,PetID),
INTERLEAVE IN PARENT Owners ON DELETE CASCADE
ENDOFFILE
- 다음 명령어를 실행하여 Spanner 인스턴스와 데이터베이스를 만듭니다.
gcloud spanner instances create test-spanner-instance --config=regional-{{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}} --description="test-spanner-instance" --processing-units=100
gcloud spanner databases create pets-db --instance=test-spanner-instance --database-dialect=GOOGLE_STANDARD_SQL --ddl-file=./pets-db-schema.sql
- 다음 명령어를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 몇 개의 테스트 레코드를 추가합니다.
owner_uuid=$(cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid)
gcloud spanner rows insert --table=Owners --database=pets-db --instance=test-spanner-instance --data=OwnerID=$owner_uuid,OwnerName=Doug
gcloud spanner rows insert --table=Pets --database=pets-db --instance=test-spanner-instance --data=PetID=$(cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid),OwnerID=$owner_uuid,PetName='Noir',PetType='Dog',Breed='Schnoodle'
gcloud spanner rows insert --table=Pets --database=pets-db --instance=test-spanner-instance --data=PetID=$(cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid),OwnerID=$owner_uuid,PetName='Bree',PetType='Dog',Breed='Mutt'
gcloud spanner rows insert --table=Pets --database=pets-db --instance=test-spanner-instance --data=PetID=$(cat /proc/sys/kernel/random/uuid),OwnerID=$owner_uuid,PetName='Gigi',PetType='Dog',Breed='Retriever'
작업 2. Spanner에서 읽을 Cloud Run 함수 만들기
- 다음 명령어를 사용하여 첫 번째 Cloud Run 함수의 폴더를 만듭니다.
mkdir ~/lab-files/spanner_get_pets
cd ~/lab-files/spanner_get_pets
- 애플리케이션에 사용할 2가지 파일(
main.py와 requirements.txt)을 만듭니다.
touch main.py requirements.txt
-
편집기 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 방금 만든
lab-files/spanner_get_pets/requirements.txt 파일에 다음 코드를 추가합니다.
google-cloud-spanner==3.27.0
-
lab-files/spanner_get_pets/main.py 파일에 데이터베이스에서 반려동물 데이터를 읽고 반환하는 코드를 다음과 같이 추가합니다.
from google.cloud import spanner
instance_id = 'test-spanner-instance'
database_id = 'pets-db'
client = spanner.Client()
instance = client.instance(instance_id)
database = instance.database(database_id)
def spanner_get_pets(request):
query = """SELECT OwnerName, PetName, PetType, Breed
FROM Owners
JOIN Pets ON Owners.OwnerID = Pets.OwnerID;"""
outputs = []
with database.snapshot() as snapshot:
results = snapshot.execute_sql(query)
output = '<div>OwnerName,PetName,PetType,Breed</div>'
outputs.append(output)
for row in results:
output = '<div>{},{},{},{}</div>'.format(*row)
outputs.append(output)
return '\n'.join(outputs)
-
터미널 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 그리고 다음 명령어를 사용하여 Cloud Run 함수를 배포합니다. 트리거는 함수 호출을 위한 URL이 생성되는 HTTP 트리거입니다. (이 명령어는 실행이 완료되는 데 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.)
gcloud functions deploy spanner_get_pets --runtime python310 --trigger-http --region={{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}} --quiet
- Cloud Run 함수를 배포하는 명령어가 완료되면 다음 명령어를 사용하여 Cloud Run 함수를 테스트하세요. 이제 테스트 데이터가 반환됩니다.
curl -m 70 -X GET https://{{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}}-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.cloudfunctions.net/spanner_get_pets -H "Authorization: bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
작업 3. Spanner에 쓰는 Cloud Run 함수 만들기
- 다음 명령어를 사용하여 두 번째 Cloud Run 함수의 폴더를 만듭니다.
mkdir ~/lab-files/spanner_save_pets
cd ~/lab-files/spanner_save_pets
- 애플리케이션에 사용할 2가지 파일(
main.py와 requirements.txt)을 만듭니다.
touch main.py requirements.txt
-
편집기 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 방금 만든
lab-files/spanner_save_pets/requirements.txt 파일에 다음 코드를 추가합니다.
google-cloud-spanner==3.27.0
-
lab-files/spanner_save_pets/main.py 파일에 데이터베이스에서 반려동물 데이터를 읽고 반환하는 코드를 다음과 같이 추가합니다.
from google.cloud import spanner
import base64
import uuid
import json
instance_id = 'test-spanner-instance'
database_id = 'pets-db'
client = spanner.Client()
instance = client.instance(instance_id)
database = instance.database(database_id)
def spanner_save_pets(event, context):
pubsub_message = base64.b64decode(event['data']).decode('utf-8')
data = json.loads(pubsub_message)
# Check to see if the Owner already exists
with database.snapshot() as snapshot:
results = snapshot.execute_sql("""
SELECT OwnerID FROM OWNERS
WHERE OwnerName = @owner_name""",
params={"owner_name": data["OwnerName"]},
param_types={"owner_name": spanner.param_types.STRING})
row = results.one_or_none()
if row != None:
owner_exists = True
owner_id = row[0]
else:
owner_exists = False
owner_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# Need a UUID for the new pet
pet_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
def insert_owner_pet(transaction, data, owner_exists):
try:
row_ct = 0
params = { "owner_id": owner_id,
"owner_name": data["OwnerName"],
"pet_id": pet_id,
"pet_name": data["PetName"],
"pet_type": data["PetType"],
"breed": data["Breed"],
}
param_types = { "owner_id": spanner.param_types.STRING,
"owner_name": spanner.param_types.STRING,
"pet_id": spanner.param_types.STRING,
"pet_name": spanner.param_types.STRING,
"pet_type": spanner.param_types.STRING,
"breed": spanner.param_types.STRING,
}
# Only add the Owner if they don't exist already
if not owner_exists:
row_ct = transaction.execute_update(
"""INSERT Owners (OwnerID, OwnerName) VALUES (@owner_id, @owner_name)""",
params=params,
param_types=param_types,)
# Add the pet
row_ct += transaction.execute_update(
"""INSERT Pets (PetID, OwnerID, PetName, PetType, Breed) VALUES (@pet_id, @owner_id, @pet_name, @pet_type, @breed)
""",
params=params,
param_types=param_types,)
except:
row_ct = 0
return row_ct
row_ct = database.run_in_transaction(insert_owner_pet, data, owner_exists)
print("{} record(s) inserted.".format(row_ct))
-
터미널 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 이 Cloud Run 함수는 Pub/Sub 메시지에서 트리거됩니다. 이 함수가 작동하려면 먼저 다음 명령어로 Pub/Sub 주제를 만들어야 합니다.
gcloud pubsub topics create new-pet-topic
- 다음 명령어를 사용해 Cloud Run 함수를 배포합니다. (이 명령어는 실행이 완료되는 데 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.)
gcloud functions deploy spanner_save_pets --runtime python310 --trigger-topic=new-pet-topic --region={{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}} --quiet
- 명령어 실행이 완료되면 콘솔에서 Pub/Sub 서비스로 이동하여 new-pet-topic 주제를 클릭하고 세부정보를 봅니다.
세부정보 페이지에서 메시지 탭을 클릭한 다음 메시지 게시 버튼을 클릭합니다.
아래 메시지를 입력한 다음 게시 버튼을 클릭합니다. 참고: 메시지는 JSON 형식이어야 하며 여기에 나온 대로 올바른 스키마를 사용해야 함수가 제대로 작동합니다.
{"OwnerName": "Jean", "PetName": "Sally", "PetType": "Frog", "Breed": "Green"}
- 이전에 실행한
curl 명령어를 사용하여 spanner_gets_pets Cloud Run 함수를 트리거합니다. 새로운 소유자인 Jean과 반려 개구리 Sally가 추가되었는지 확인합니다.
curl -m 70 -X GET https://{{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}}-${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT}.cloudfunctions.net/spanner_get_pets -H "Authorization: bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
작업 4. Spanner 에뮬레이터 시작하기
- Cloud Shell 터미널에서 다음 명령어를 실행하여 Spanner 에뮬레이터를 설치하고 시작합니다.
sudo apt-get install google-cloud-sdk-spanner-emulator
gcloud emulators spanner start
- 에뮬레이터가 터미널을 제어하므로 Cloud Shell 툴바에서 + 아이콘을 클릭하여 새 터미널 탭을 엽니다. 다음 명령어를 실행하여 Cloud SDK가 에뮬레이터를 사용하도록 구성합니다.
gcloud config configurations create emulator
gcloud config set auth/disable_credentials true
gcloud config set project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
gcloud config set api_endpoint_overrides/spanner http://localhost:9020/
- gcloud를 사용해 인스턴스와 데이터베이스를 만듭니다. 단, 이 명령어는 현재 클라우드의 Spanner가 아니라 에뮬레이터를 사용합니다. 명령어를 전체가 아니라 개별적으로 실행합니다.
cd ~/lab-files
gcloud spanner instances create emulator-instance --config=emulator-config --description="EmulatorInstance" --nodes=1
gcloud spanner databases create pets-db --instance=emulator-instance --database-dialect=GOOGLE_STANDARD_SQL --ddl-file=./pets-db-schema.sql
- Python 클라이언트 라이브러리의 코드가 에뮬레이터를 사용하려면
SPANNER_EMULATOR_HOST 환경 변수를 설정해야 합니다. 이를 위해 다음 코드를 실행합니다.
export SPANNER_EMULATOR_HOST=localhost:9010
작업 5. Spanner Pets 데이터베이스용 REST API 작성하기
- Cloud Run 프로그램 파일을 저장할 폴더를 만들고 필요한 파일을 추가합니다.
mkdir ~/lab-files/cloud-run
cd ~/lab-files/cloud-run
touch Dockerfile main.py requirements.txt
-
편집기 열기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 방금 만든
lab-files/cloud-run/requirements.txt 파일에 다음 코드를 추가합니다.
Flask==3.0.3
Flask-RESTful==0.3.10
google-cloud-spanner==3.27.0
gunicorn==22.0.0
-
main.py에 다음을 추가합니다. 이 코드는 Python Flask와 Flask-RESTful 라이브러리를 사용하여 Pets 데이터베이스용 REST API를 빌드합니다.
참고: 파일 상단부에서 환경 변수를 사용하는 부분(11~20행)을 확인합니다. Cloud Run에 배포할 때 이러한 변수가 실제 Spanner 데이터베이스를 가리키도록 설정합니다. 변수를 설정하지 않으면 기본적으로 에뮬레이터가 사용됩니다.
import os
import uuid
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
from flask_restful import Api, Resource
from google.api_core import exceptions
from google.cloud import spanner
from werkzeug.exceptions import BadRequest, NotFound
# --- Configuration ---
# Use emulator settings by default, but override with environment variables if they exist.
INSTANCE_ID = os.environ.get("INSTANCE_ID", "emulator-instance")
DATABASE_ID = os.environ.get("DATABASE_ID", "pets-db")
# --- Database Repository ---
class SpannerRepository:
"""
A repository class to handle all database interactions with Google Cloud Spanner.
This separates database logic from the API/view layer.
"""
def __init__(self, instance_id, database_id):
spanner_client = spanner.Client()
self.instance = spanner_client.instance(instance_id)
self.database = self.instance.database(database_id)
def list_all_pets(self):
"""Retrieves all pets with their owner information."""
query = """
SELECT o.OwnerID, o.OwnerName, p.PetID, p.PetName, p.PetType, p.Breed
FROM Owners o JOIN Pets p ON o.OwnerID = p.OwnerID
"""
with self.database.snapshot() as snapshot:
results = snapshot.execute_sql(query)
# 1. Materialize the iterator into a list of rows.
# Each 'row' in this list is a regular Python list of values.
rows = list(results)
# 2. If there are no rows, the metadata might be incomplete.
# This check prevents the original 'NoneType' error.
if not rows:
return []
# 3. If we have rows, the metadata is guaranteed to be available.
# Get the column names from the result set's metadata.
# Note: results.metadata is the correct attribute.
keys = [field.name for field in results.metadata.row_type.fields]
# 4. Zip the keys with each row's list of values to create dicts.
return [dict(zip(keys, row)) for row in rows]
def get_pet_by_id(self, pet_id):
"""Retrieves a single pet by its ID."""
query = """
SELECT o.OwnerID, o.OwnerName, p.PetID, p.PetName, p.PetType, p.Breed
FROM Owners o JOIN Pets p ON o.OwnerID = p.OwnerID
WHERE p.PetID = @pet_id
"""
params = {"pet_id": pet_id}
param_types = {"pet_id": spanner.param_types.STRING}
with self.database.snapshot() as snapshot:
results = snapshot.execute_sql(
query, params=params, param_types=param_types
)
# results.one_or_none() returns a special Row object (not a list)
# that has a .keys() method, so this is correct and simpler.
row = results.one_or_none()
if not row:
return None
return dict(zip(row.keys(), row))
def create_pet_and_owner(self, data):
"""
Creates a new pet. If the owner doesn't exist, creates the owner as well.
This entire operation is performed in a single transaction.
"""
def _tx_create_pet(transaction):
pet_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
owner_name = data["OwnerName"]
owner_result = transaction.execute_sql(
"SELECT OwnerID FROM Owners WHERE OwnerName = @name",
params={"name": owner_name},
param_types={"name": spanner.param_types.STRING},
).one_or_none()
if owner_result:
owner_id = owner_result[0]
else:
owner_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
transaction.insert(
"Owners",
columns=("OwnerID", "OwnerName"),
values=[(owner_id, owner_name)],
)
pet_columns = ["PetID", "OwnerID", "PetName", "PetType", "Breed"]
pet_values = [
pet_id,
owner_id,
data["PetName"],
data["PetType"],
data["Breed"],
]
transaction.insert("Pets", columns=pet_columns, values=[pet_values])
new_pet_data = {
"PetID": pet_id,
"OwnerID": owner_id,
"OwnerName": owner_name,
"PetName": data["PetName"],
"PetType": data["PetType"],
"Breed": data["Breed"],
}
return new_pet_data
return self.database.run_in_transaction(_tx_create_pet)
def delete_pet_by_id(self, pet_id):
"""Deletes a single pet by its ID in a transaction."""
def _tx_delete_pet(transaction):
return transaction.execute_update(
"DELETE FROM Pets WHERE PetID = @pet_id",
params={"pet_id": pet_id},
param_types={"pet_id": spanner.param_types.STRING},
)
return self.database.run_in_transaction(_tx_delete_pet)
def delete_all_pets_and_owners(self):
"""Deletes all owners, which cascades to delete all pets."""
def _tx_delete_all(transaction):
return transaction.execute_update("DELETE FROM Owners WHERE true")
return self.database.run_in_transaction(_tx_delete_all)
# --- API Resources ---
db_repo = SpannerRepository(INSTANCE_ID, DATABASE_ID)
class PetsList(Resource):
def get(self):
"""Returns a list of all pets."""
pets = db_repo.list_all_pets()
return jsonify(pets)
def post(self):
"""Creates a new pet and possibly a new owner."""
try:
data = request.get_json(force=True)
required_fields = ["OwnerName", "PetName", "PetType", "Breed"]
if not all(field in data for field in required_fields):
raise BadRequest("Missing required fields in JSON payload.")
except BadRequest as e:
return {"message": str(e)}, 400
try:
new_pet = db_repo.create_pet_and_owner(data)
return new_pet, 201
except exceptions.GoogleAPICallError as e:
return {"message": "Database transaction failed", "error": str(e)}, 500
def delete(self):
"""Deletes all owners and pets."""
deleted_count = db_repo.delete_all_pets_and_owners()
return {"message": f"{deleted_count} owner record(s) deleted (pets cascaded)."}, 200
class Pet(Resource):
def get(self, pet_id):
"""Returns a single pet by ID."""
pet = db_repo.get_pet_by_id(pet_id)
if pet:
return jsonify(pet)
raise NotFound("Pet with the specified ID was not found.")
def delete(self, pet_id):
"""Deletes a single pet by ID."""
try:
deleted_count = db_repo.delete_pet_by_id(pet_id)
if deleted_count > 0:
return {"message": f"Pet with ID {pet_id} was deleted."}, 200
raise NotFound("Pet with the specified ID was not found.")
except exceptions.NotFound:
raise NotFound("Pet with the specified ID was not found.")
def patch(self, pet_id):
"""This endpoint is not implemented."""
return {"message": "Update operation is not implemented."}, 501
# --- Flask App Initialization ---
def create_app():
"""Application factory to create and configure the Flask app."""
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
# API Resource routing
api.add_resource(PetsList, "/pets")
api.add_resource(Pet, "/pets/<string:pet_id>")
# Centralized error handling
@app.errorhandler(NotFound)
def handle_not_found(e):
return jsonify({"message": str(e)}), 404
@app.errorhandler(BadRequest)
def handle_bad_request(e):
return jsonify({"message": str(e)}), 400
@app.errorhandler(Exception)
def handle_generic_error(e):
app.logger.error(f"An unhandled exception occurred: {e}", exc_info=True)
return jsonify({"message": "An internal server error occurred."}), 500
return app
app = create_app()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Use debug=False in a production environment
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=8080, debug=True)
-
터미널 열기 버튼을 클릭한 후 다음 코드를 실행하여 필요한 패키지를 설치합니다.
pip install -r requirements.txt
- 이제 터미널에서 다음 코드를 실행하여 프로그램을 시작합니다.
python main.py
-
Cloud Shell 툴바에서 + 아이콘을 다시 클릭하여 세 번째 터미널 탭을 엽니다.
-
curl을 사용하여 API를 테스트할 수 있습니다. 먼저 HTTP POST 명령어를 사용하여 레코드를 추가합니다.
curl -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Sue", "PetName": "Sparky", "PetType": "Cat", "Breed": "Alley"}' http://localhost:8080/pets
curl -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Sue", "PetName": "Pickles", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Shepherd"}' http://localhost:8080/pets
curl -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Doug", "PetName": "Noir", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Schnoodle"}' http://localhost:8080/pets
curl -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Doug", "PetName": "Bree", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Mutt"}' http://localhost:8080/pets
curl -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Joey", "PetName": "Felix", "PetType": "Cat", "Breed": "Tabby"}' http://localhost:8080/pets
- HTTP GET 명령어를 사용하여 레코드가 추가되었는지 확인합니다. 레코드는 JSON 형식으로 반환되어야 합니다.
curl http://localhost:8080/pets
참고: 단계를 누락했거나 원하는 출력이 표시되지 않는 경우 Cloud Shell을 사용하여 작업 4부터 단계를 다시 수행해 보세요.
-
exit를 입력하여 세 번째 터미널 탭을 닫은 다음 Ctrl + C를 입력하여 두 번째 터미널 탭에서 Python 프로그램을 중지합니다. exit를 입력하여 두 번째 탭을 닫습니다. 첫 번째 터미널 탭으로 돌아가서 Ctrl + C를 입력해 에뮬레이터를 중지합니다.
참고: 이러한 레코드가 에뮬레이터에 추가되었습니다. 다음으로 Cloud Run에 배포하고 실제 Spanner 인스턴스를 사용합니다.
작업 6. Cloud Run에 앱 배포하기
- Cloud Run에 배포하려면 Docker 이미지가 필요합니다. 먼저 디렉터리를 cloud-run 폴더로 변경합니다.
cd ~/lab-files/cloud-run
- Docker 이미지를 만들려면 Dockerfile 파일에 안내를 추가해야 합니다. 편집기 열기 버튼을 클릭하고 Dockerfile 파일을 연 후 다음 코드를 붙여넣습니다.
FROM python:3.9
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN pip install gunicorn
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
ENV PORT=8080
CMD exec gunicorn --bind :$PORT --workers 1 --threads 8 main:app
- 터미널로 돌아가 다음 코드를 실행하여 Docker 이미지를 만듭니다. (현재 ~/lab-files/cloud-run 폴더에 있는지 확인합니다.)
gcloud builds submit --tag=gcr.io/$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT/spanner-pets-api:v1.0 .
-
API 탐색 및 사용 설정을 통해 프로젝트에 Cloud Run이 사용 설정되어 있는지 확인합니다.
-
이제 다음 명령어를 사용하여 Cloud Run 애플리케이션을 배포합니다. 코드가 not the emulator(에뮬레이터가 아니라) Cloud Spanner 인스턴스를 사용하도록 명령어에 환경 변수가 설정된 방식을 확인하세요. 명령어가 완료되는 데 몇 분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.
gcloud run deploy spanner-pets-api --image gcr.io/$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT/spanner-pets-api:v1.0 --update-env-vars INSTANCE_ID=test-spanner-instance,DATABASE_ID=pets-db --region={{{project_0.default_region|place_holder_text}}}
- 명령어 실행이 완료되면 서비스 URL을 기록하고 클립보드에 복사합니다. 에뮬레이터와 마찬가지로 curl 명령어를 사용하여 API를 테스트할 수 있습니다. 우선 아래와 같이 URL을 저장할 변수를 만듭니다. 이때 전체 자리표시자(<YOUR_SERVICE_URL_HERE>) 대신
https://...를 포함한 전체 URL을 붙여넣습니다.
pets_url=<YOUR_SERVICE_URL_HERE>
- curl을 사용하여 몇몇 레코드를 추가합니다.
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Sue", "PetName": "Sparky", "PetType": "Cat", "Breed": "Alley"}' $pets_url/pets
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Sue", "PetName": "Pickles", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Shepherd"}' $pets_url/pets
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Doug", "PetName": "Noir", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Schnoodle"}' $pets_url/pets
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Doug", "PetName": "Bree", "PetType": "Dog", "Breed": "Mutt"}' $pets_url/pets
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X POST --data '{"OwnerName": "Joey", "PetName": "Felix", "PetType": "Cat", "Breed": "Tabby"}' $pets_url/pets
-
레코드가 추가되었습니다. 콘솔에서 Cloud Run 서비스로 이동해 내 서비스를 클릭하여 세부정보를 확인하고 로그를 살펴봅니다. 여기에서 전송한 각 요청이 기록된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
-
레코드가 추가되었는지 확인할 수도 있습니다.
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" $pets_url/pets
-
Spanner로 이동하여 인스턴스와 데이터베이스를 살펴봅니다.
-
API는 DELETE도 구현합니다. 모든 데이터를 삭제하려면 터미널로 돌아가 다음 명령어를 입력합니다.
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-identity-token)" -X DELETE $pets_url/pets
- 더 이상 요금이 청구되지 않도록 콘솔에서 Spanner 인스턴스를 삭제합니다.
수고하셨습니다. 이 실습에서는 Spanner 데이터베이스를 활용하는 애플리케이션을 작성하여 Cloud Run Functions와 Cloud Run 모두에 배포했습니다. 또한 개발 환경에서 사용할 Spanner 에뮬레이터를 설치하고 구성한 후 사용 설정했습니다.
실습 종료
실습을 완료하면 실습 종료를 클릭합니다. Qwiklabs에서 사용된 리소스를 자동으로 삭제하고 계정을 지웁니다.
실습 경험을 평가할 수 있습니다. 해당하는 별표 수를 선택하고 의견을 입력한 후 제출을 클릭합니다.
별점의 의미는 다음과 같습니다.
- 별표 1개 = 매우 불만족
- 별표 2개 = 불만족
- 별표 3개 = 중간
- 별표 4개 = 만족
- 별표 5개 = 매우 만족
의견을 제공하고 싶지 않다면 대화상자를 닫으면 됩니다.
의견이나 제안 또는 수정할 사항이 있다면 지원 탭을 사용하세요.
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google 및 Google 로고는 Google LLC의 상표입니다. 기타 모든 회사명 및 제품명은 해당 업체의 상표일 수 있습니다.