Checkpoints
Set up a Google Cloud Storage bucket
/ 20
Upload the data files to your Cloud Storage bucket
/ 20
Run a single-instance trainer in the cloud
/ 20
Create a Cloud ML Engine model
/ 20
Create a version v1 of your model
/ 20
Vertex AI Workbench Notebook: Qwik Start
GSP076
Overview
This lab will give you hands-on practice with TensorFlow 2.x model training, both locally and on Vertex AI Workbench. After training, you will learn how to deploy your model to Vertex AI for serving (prediction). You'll train your model to predict the income category of a person using the United States Census Income Dataset.
This lab gives you an introductory, end-to-end experience of training and prediction on Vertex AI. The lab will use a census dataset to:
- Create a TensorFlow 2.x training application and validate it locally.
- Run your training job on a single worker instance in the cloud.
- Deploy a model to support prediction.
- Request an online prediction and see the response.
What you will build
The sample builds a classification model for predicting income category based on the United States Census Income Dataset. The two income categories (also known as labels) are:
- >50K — Greater than 50,000 dollars
- <=50K — Less than or equal to 50,000 dollars
The sample defines the model using the Keras Sequential API. The sample defines the data transformations particular to the census dataset, then assigns these (potentially) transformed features to either the DNN or the linear portion of the model.
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account. -
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}} You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}} You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials. Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges. -
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

Task 1. Launch Vertex AI Workbench notebook
To create and launch a Vertex AI Workbench notebook:
-
In the Navigation Menu
, click Vertex AI > Workbench.
-
On the Workbench page, click Enable Notebooks API (if it isn't enabled yet).
-
Click on User-Managed Notebooks tab then, click Create New.
-
Name the notebook.
-
Set Region to
and Zone to . -
In the New instance menu, choose the latest version of TensorFlow Enterprise 2.11 in Environment.
-
Click Advanced Options to edit the instance properties.
-
Click Machine type and then select e2-standard-2 for Machine type.
-
Leave the remaining fields at their default and click Create.
After a few minutes, the Workbench page lists your instance, followed by Open JupyterLab.
- Click Open JupyterLab to open JupyterLab in a new tab. If you get a message saying beatrix jupyterlab needs to be included in the build, just ignore it.
Task 2. Clone the example repo within your Workbench instance
To clone the training-data-analyst repository in your JupyterLab instance:
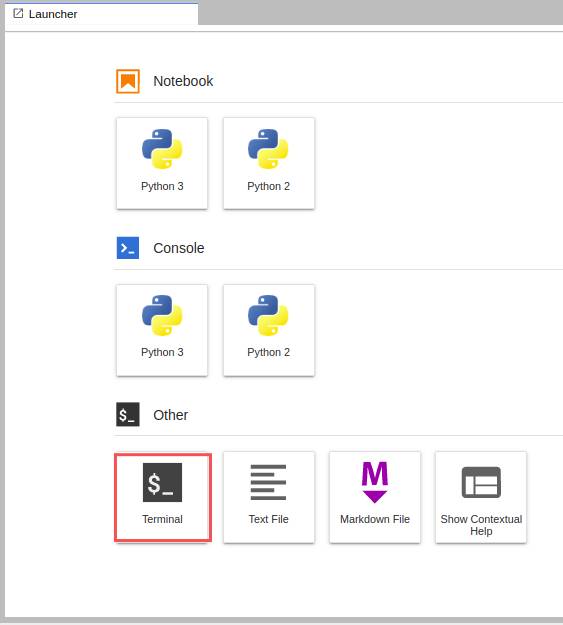
- In JupyterLab, click the Terminal icon to open a new terminal.
- At the command-line prompt, type the following command and press ENTER:
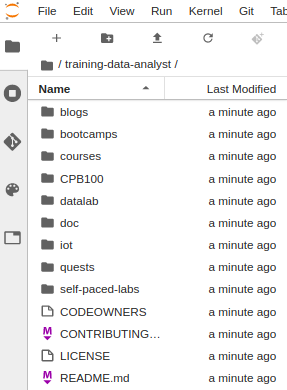
- To confirm that you have cloned the repository, in the left panel, double click the
training-data-analystfolder to see its contents.
It will take several minutes for the notebook to clone.
Navigate to the example notebook
-
Navigate to
training-data-analyst/self-paced-labs/ai-platform-qwikstartand openai_platform_qwik_start.ipynb. -
On the notebook toolbar, navigate to Edit > Clear All Outputs and then Run the cells one by one.
When prompted, come back to these instructions to check your progress.
Task 3. Run your training job in the cloud
There are additional steps to read in the notebook. Read these instructions carefully including the comments in the cells with code to ensure you are completing each step correctly.
Test completed tasks - step 3.1
- Click Check my progress to verify your performed task.
- Click Check my progress to verify your performed task.
Test completed tasks - step 3.2
Click Check my progress to verify your performed task.
Test completed tasks - step 3.3
- Click Check my progress to verify your performed task.
- Click Check my progress to verify your performed task.
Task 4. Test your understanding
Below are multiple choice questions to reinforce your understanding of this lab's concepts. Answer them to the best of your abilities.
Congratulations!
In this lab you've learned how to train a TensorFlow model both locally and on Vertex AI, and then how to use your trained model for prediction.
Next steps
- Sign up for the full Coursera Course on Machine Learning.
- Explore a wide range of TensorFlow tutorials.
- You can read more about wide and deep models in the Google Research Blog post named Wide & Deep Learning: Better Together with TensorFlow.
- Get your own version of Tensorflow.
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated April 26, 2024
Lab Last Tested April 26, 2024
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.