
Before you begin
- Labs create a Google Cloud project and resources for a fixed time
- Labs have a time limit and no pause feature. If you end the lab, you'll have to restart from the beginning.
- On the top left of your screen, click Start lab to begin
Set up the Cloud Storage bucket
/ 40
Clone the Dataflow Job
/ 30
Set up a streaming architecture on GCP
/ 30
This lab gives you hands-on experience deploying SingleStoreDB and combining it with Google Cloud's cloud native products like Pub/Sub, Dataflow and Cloud Storage. To demonstrate these product features, work with the NYC public taxi dataset.
The flow of the lab is to first deploy the SingleStoreDB through your local browser and create the appropriate schema. Then, use Pub/Sub to push the data to Cloud Storage in real time with the help of Dataflow. The data generated and stored in object storage is consumed using SingleStoreDB's native pipeline. Once SingleStoreDB has ingested the data, you run queries and interact with SingleStore.
In this lab, you learn how to perform the following tasks:
Prerequisites
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources are made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a dialog opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details pane with the following:
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details pane.
Click Next.
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

At this point you should be logged into the Google Cloud console in an Incognito window.
On the upper left corner click + Create New and Select Deployment.
On the Create Workspace page, configure the following settings:
Your configuration should look like this:
Click Next.
On the Workspace Details page, leave the default settings, and click Create Workspace.
Wait a few minutes as your workspace spins up. It generates a sample database for you, which you are not going to use for this lab.
Before connecting to the SingleStore Workspace, navigate back to the Google Cloud console.
Open a new Cloud Shell window by clicking the Activate Cloud Shell (
In Cloud Shell, run the following commands to clone the GitHub repository to download the code for the workshop.
On the Connect to Workspace page, first copy the password that was generated for you. There is a copy icon next to the password. It is a good idea to store this in a local file because you need it later in this lab.
Click the Copy icon to the right of the MySQL Command. This copies the command to your clipboard.
The MySQL command should resemble: mysql -u admin -h svc-b675ae2f-b129-4baf-86ca-0a03c2c31d19-dml.gcp-virginia-1.svc.singlestore.com -P 3306 --default-auth=mysql_native_password --password
Navigate back to the Google Cloud console and your Cloud Shell instance.
Paste the MySQL command into the terminal.
Enter the password that you copied earlier if prompted. You're now at a mysql> prompt.
In this section, you build the table schemas.
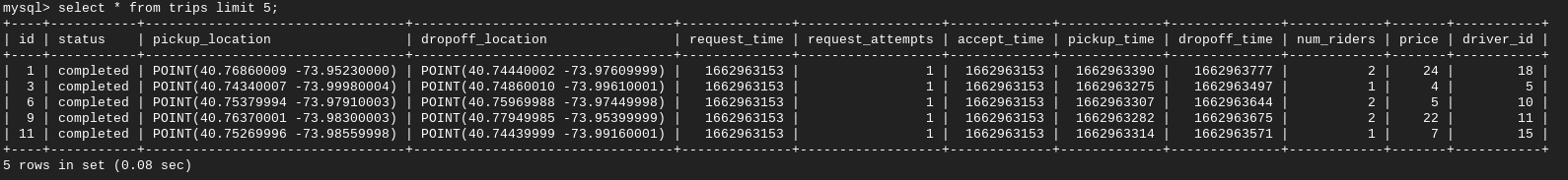
Use the following DDL to create a new database named nyc_taxi.
You should get results similar to the following.
Output:
You have created the Schema and the Database tables are listed.
The output of this query is "Empty set" or "0". This is because you have only created the Schema and the Table is empty.
Pause here for a second. You've successfully created the SingleStore Database and connected to it. The Schema is set up but there is no data yet.
If you have extra time, feel free to poke around and explore SingleStore!
In today's lab, you use the NYC Taxi data, this data can be found in BigQuery's public datasets or on the NYC Open Data website.
This data has been put in a Cloud Storage bucket for you ahead of time, so there is no need for you to download/import this into Google Cloud. You can explore the data if you so wish.
The NYC Open Data website provides free datasets related to New York City, including taxi, education, police data and more.
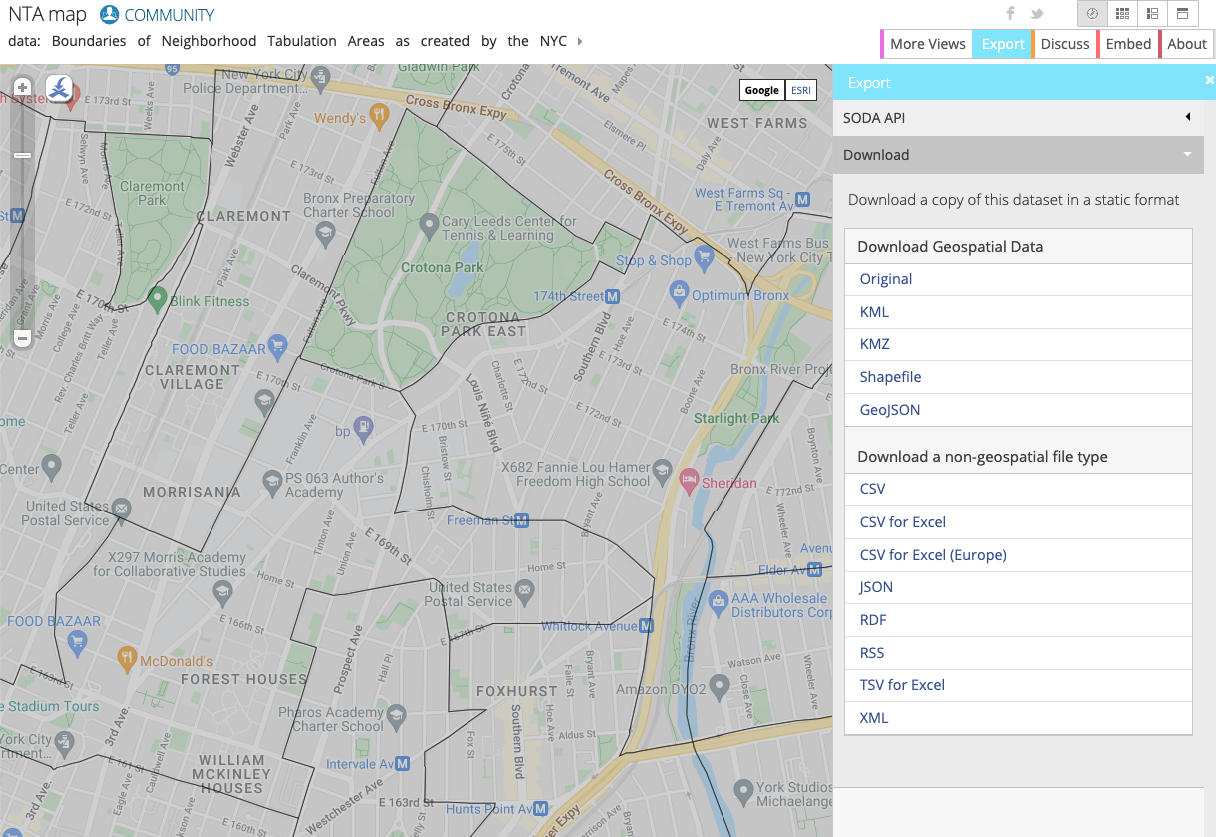
In this lab, you work with the NYC Department of City Planning's Neighborhood Tabulation Areas (NTAs) which provides information on approximate zones and neighborhoods in NYC. You use this in combination with NYC Taxi data to see where passengers were picked up and dropped off.
On the website you can visualize the data by neighborhood:

In Google Cloud, the two main ways to set up resources are through the GUI and CLI. In this lab, you use the CLI to create the bucket and get the latest neighborhood data from NYC taxi cab website.
If prompted, click Authorize.
Notice there is already another bucket created in your project. Don't worry about this bucket, it's a staging/temp storage location for Dataflow.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Pub/Sub and Dataflow resources have been pre-populated in your project. To view them, use the search box at the top of your Cloud console to find Pub/Sub and Dataflow, respectively.
Click on the job and click Clone to run this exact job. Rename it and check the job info (which you've pre populated since you cloned it) so you know what you're running. Scroll down and click Run Job.
Return to Dataflow jobs and make sure your job has a status of "running".
You've now simulated live data streaming! As an example, if you were to upload more data to GCS and Pull in Pub/Sub, Dataflow would be moving the data live.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
A common streaming architecture on Google Cloud consists of Pub/Sub > Dataflow > GCS. In this task, you set this up and then plug SingleStore into GCS.
Navigate back to Dataflow.
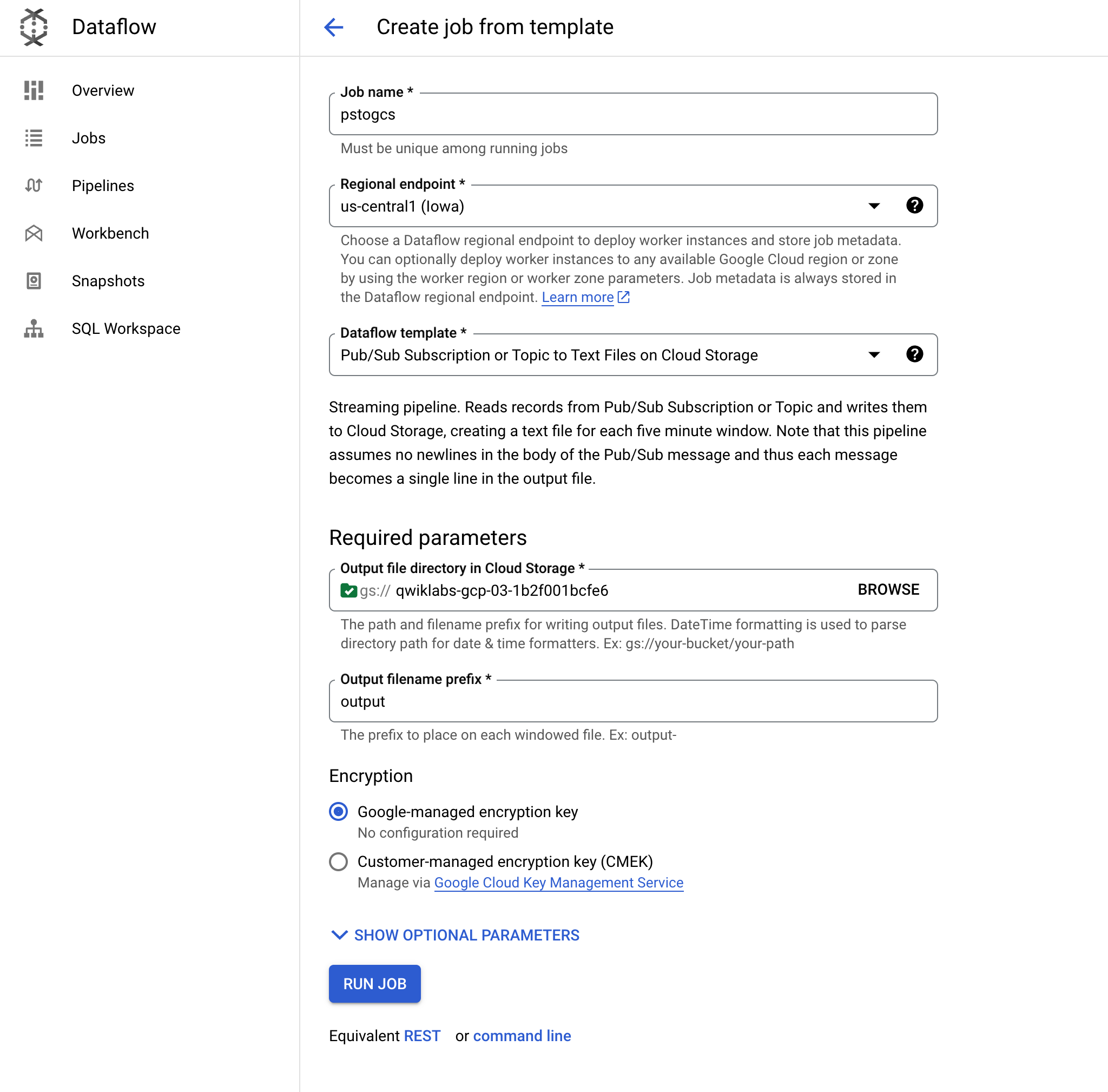
Click Create a job from template and name it pstogcs (PubSub to GCS).
Select the Regional endpoint as
Select the following Dataflow template: Pub/Sub Subscription or Topic to Text Files on Cloud Storage. A number of options appear, so you may need to Filter for it.
For Target, click Browse, and select the bucket you created earlier, called
Leave the output filename prefix as output. This is to mark the output files clearly.
Expand Optional Source Parameters. For Pub/Sub input subscription, select the Taxi-sub that you just saw messages coming into. No need to include input topic.
Leave the defaults for everything else, then go to the bottom of the page, and click RUN JOB.
This Dataflow job should read the messages you saw earlier in Pub/Sub and Stream them into your Cloud Storage bucket.
Go to Cloud Storage > Buckets and open your bucket,
Click on the output file and select Download. You should see Taxi data that includes names, coordinates, and times

Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You can use Gemini Code Assist in an integrated development environment (IDE) such as Cloud Shell to receive guidance on code or solve problems with your code. Before you can start using Gemini Code Assist, however, you need to enable it.
In the Cloud Shell Editor, navigate to Cloud Code > Help and Feedback > Change Settings.
In the Settings, search for Gemini Code Assist.
Locate and ensure that the checkbox is selected for Geminicodeassist: Enable, and close the Settings.
Click Cloud Code - No Project in the status bar at the bottom of the screen.
Authorize the plugin as instructed. If a project is not automatically selected, click Select a Google Cloud Project, and choose
Verify that your Google Cloud project (
You now need to create a Key to connect this private Cloud Storage bucket to SingleStore.
In Cloud Storage, go to Settings (in the Navigation menu).
Click the Interoperability tab. At the bottom, click Create a Key.
Next, you ingest data into SingleStore with pipelines and start a stored procedure.
To create initial SingleStore pipelines:
This action enables Gemini Code Assist, as indicated by the presence of the 
Click the Gemini Code Assist: Smart Actions 
Gemini Code Assist opens a chat pane with the prefilled prompt of Explain this. In the inline text box of the Code Assist chat, replace the prefilled prompt with the following, and click Send:
The explanation for the code in the create_nyctaxi_pipelines.dml file appears in the Gemini Code Assist chat.
.tsv to .csv./t to ,.Your file should resemble the following:
Return to the Cloud Shell Terminal. Connect to SingleStore using the MySQL command you used earlier. You can use the same command you used earlier to connect to SingleStore.
At the MySQL prompt, run the following command to create the pipelines:
The output should resemble the following.
Output:
Output:
Report 1: Total number of trips for each neighborhood.
Report 2: The average amount of time between someone requesting a ride and that person being picked up.
Report 3: The average distance of a trip.
Report 4: The average amount of time between someone being picked up and that person being dropped off.
Report 5: The average cost of a trip.
Report 6: The average amount of time it takes from the time a driver accepts a ride to the time they pick up the passenger.
Report 7: The average number of riders per trip.
Congratulations! In this lab, you have deployed SingleStoreDB and combined it with Google Cloud's cloud native products like Pub/Sub, Dataflow, and Cloud Storage. You have also used SingleStoreDB's native pipeline to ingest data from Cloud Storage and run operational analytic queries.
You can learn more about SingleStore at SingleStore.com.
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated August 22, 2025
Lab Last Tested August 12, 2025
Copyright 2025 Google LLC. All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




This content is not currently available
We will notify you via email when it becomes available

Great!
We will contact you via email if it becomes available


One lab at a time
Confirm to end all existing labs and start this one
