Контрольні точки
Create a Compute Engine VM instance
/ 20
Install an Apache Web Server
/ 20
Install the Ops Agent
/ 30
Create an alerting policy
/ 30
Monitor a Compute Engine Virtual Machine: Qwik Start
GSP1108
Overview
In this lab you use Cloud Monitoring to generate traffic and view metrics on the predefined Apache dashboard in the Google Cloud console.
Objectives
In this lab, you learn how to perform the following tasks:
- Create a Compute Engine VM instance.
- Install an Apache Web Server.
- Install and configure the Ops Agent for the Apache Web Server.
- Generate traffic and view metrics on the predefined Apache dashboard.
- Create an alerting policy.
Task 1. Create a Compute Engine VM instance
-
In the Google Cloud console, select Navigation menu > Compute Engine > VM Instances.
-
To create a VM instance, click Create instance.
-
Fill in the fields for your instance as follows:
- In the Name field, enter
quickstart-vm. - In the Machine type field, select e2-small.
- Ensure the Boot disk is configured for Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye).
- In the Firewall field, select both Allow HTTP traffic and Allow HTTPS traffic.
- In the Name field, enter
Leave the rest of the fields at their default values.
- Click Create. When your VM is ready, it appears in the list of instances in the Instances tab.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 2. Install an Apache Web Server
To deploy an Apache Web Server on your Compute Engine VM instance, do the following:
-
To open a terminal to your instance, in the Connect column, click SSH.
-
To update the package lists on your instance, run the following command:
- To install an Apache2 HTTP Server, run the following command:
sudo apt-get install apache2 php. If asked to continue the installation, enter Y.
- Open your browser and connect to your Apache2 HTTP server by using the URL
http://EXTERNAL_IP, whereEXTERNAL_IPis the external IP address of your VM. You can find this address in the External IP column of your VM instance.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 3. Install and configure the Ops Agent
To collect logs and metrics from your Apache Web Server, install the Ops Agent by using the terminal:
-
To open a terminal to your VM instance, in the Connect column, click SSH.
-
To install the Ops Agent, run the following command:
You should notice the google-cloud-ops-agent installation succeeded.
- Copy the following command, then paste it into the terminal:
The previous command creates the configuration to collect and ingest logs and metrics from the Apache Web Server. For more information about ingesting logs from the Apache Web Server, see Configure the Ops Agent for Apache Web Server.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 4. Generate traffic and view metrics
Monitoring dashboards let you view and analyze metrics related to your services. In this quickstart, you generate metrics on your Apache Web Server and view metric data on the automatically created Apache Overview dashboard.
To generate metrics on your Apache Web Server, do the following:
-
In Google Cloud console, select Navigation menu > Compute Engine.
-
In the Connect column, click SSH to open a terminal to your VM instance.
-
To generate traffic on your Apache Web Server, run the following command:
The previous command generates traffic by making a request to the Apache Web Server every four seconds.
To view the Apache Overview dashboard, do the following:
-
In the Google Cloud console, search for Monitoring in the top search bar and navigate to the Monitoring service.
-
In the navigation pane, select Dashboards.
-
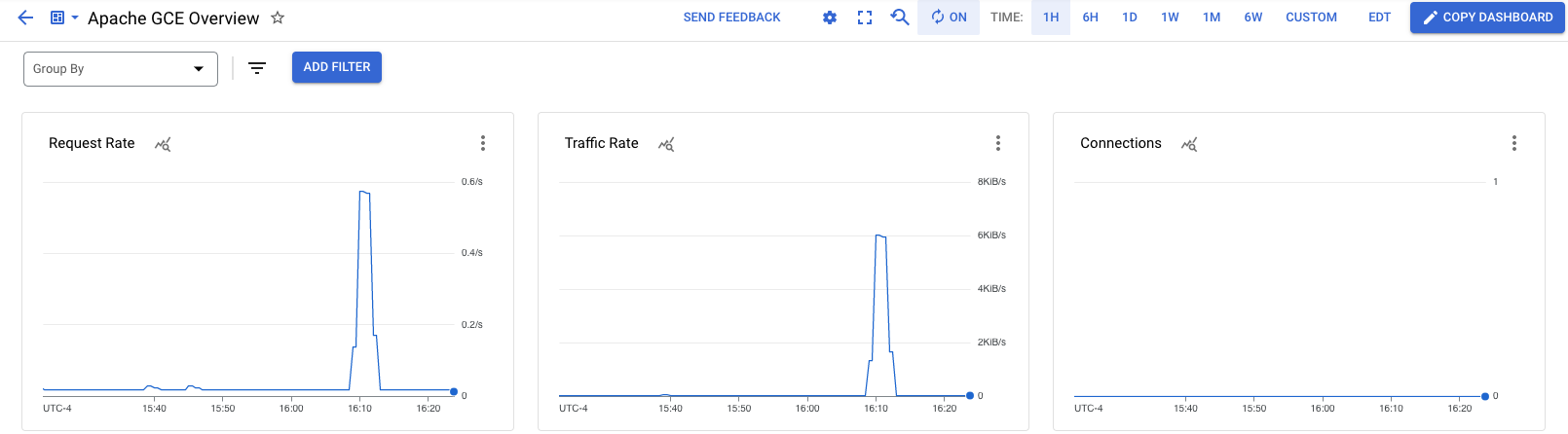
In All Dashboards, select the Apache GCE Overview dashboard. The dashboard opens.
In the dashboard, there are several charts that contain information about your Apache and Compute Engine integration:
Task 5. Create an alerting policy
-
To set up an email notification channel, do the following:
- In Google Cloud console, select Navigation menu > Monitoring select Alerting and then click Edit notification channels.
- Scroll down the page and click on Add new for Email.
-
Name the Email Channel:
An email address you have access to - Enter the Display name.
- Click Save.
To create an alerting policy that monitors a metric and sends an email notification when the traffic rate on your Apache Web Server exceeds 4 KiB/s, do the following:
-
In Google Cloud console, select Navigation menu > Monitoring > Alerting and then click Create policy.
-
Select the time series to be monitored:
- Click Select a metric and enter VM instance into the filter bar.
- In the Active metric categories list, select Apache.
- In the Active metrics list, select workload/apache.traffic. Click Apply.
The chart for Apache traffic is shown.
-
In the Transform data section, select the following values and click Next:
-
Rolling window:
1 min -
Rolling window function:
rate
-
Rolling window:
-
In the Configure alert trigger section, select the following values and click Next:
-
Alert trigger:
Any time series violates -
Threshold position:
Above threshold -
Threshold value:
4000
-
Alert trigger:
-
In the Configure notifications and finalize alert section, select the following values:
-
Notification channels: Select the
Display nameyou have created earlier and click OK. -
Incident autoclose duration:
30 min -
Name the alert policy:
Apache traffic above threshold
-
Notification channels: Select the
-
Click Create policy. Your alerting policy is now active.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 6. Test the alerting policy
To test the alerting policy you just created, do the following:
-
In Google Cloud console, select Navigation menu > Compute Engine.
-
In the Connect column, click SSH to open a terminal to your VM instance.
-
In the terminal, enter the following command:
The previous command generates traffic in your Apache Web Server.
After the traffic rate threshold value of 4 KiB/s is exceeded in your Apache Web Server, an email notification is sent. It might take several minutes for this process to complete.
The email notification you receive looks similar to the following:
Congratulations!
In this lab, you learned how to install Ops Agent on a VM and use it to set an alerting policy to notify a recipient of potential issues with the instance.
Manual Last Updated March 20, 2024
Lab Last Tested March 20, 2024
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.