GSP604

Overview
This lab reviews the bitcoin transactions tied to the infamous 10,000 bitcoin pizza purchase.
This code is based on code originally written by Allen Day and modified by Sohien Dane and Meg Risdal from these Kaggle kernels (parts 1, 2, 3). You use it to visualize a directed graph representing Bitcoin transactions that follow the first known exchange of Bitcoin for goods on May 17, 2010 made by Laszlo Hanyecz.
You will use a Vertex AI Workbench instance to:
- Retrieve as many transactions as possible from BigQuery within 2 degrees of separation from the pizza exchange.
- Post-process the transactions to remove excess transactions from step 1 because the query was overly-greedy to ensure the number of table scans equals the degrees of separation.
- Visualize the directed graph.
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
Note: Use an Incognito or private browser window to run this lab. This prevents any conflicts between your personal account and the Student account, which may cause extra charges incurred to your personal account.
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
Note: If you already have your own personal Google Cloud account or project, do not use it for this lab to avoid extra charges to your account.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method.
On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account.
-
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}}
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}}
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials.
Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges.
-
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.
Note: To view a menu with a list of Google Cloud products and services, click the Navigation menu at the top-left.

Task 1. Launch Vertex Workbench Notebook
To create and launch a Vertex AI Workbench notebook:
-
In the Navigation Menu  , click Vertex AI > Workbench.
, click Vertex AI > Workbench.
-
On the Workbench page, click Enable Notebooks API (if it isn't enabled yet).
-
Click on User-Managed Notebooks tab then, click Create New.
-
Name the notebook.
-
Set Region to and Zone to .
-
In the New instance menu, choose the latest version of TensorFlow Enterprise 2.11 in Environment.
-
Click Advanced Options to edit the instance properties.
-
Click Machine type and then select e2-standard-2 for Machine type.
-
Leave the remaining fields at their default and click Create.
After a few minutes, the Workbench page lists your instance, followed by Open JupyterLab.
- Click Open JupyterLab to open JupyterLab in a new tab. If you get a message saying beatrix jupyterlab needs to be included in the build, just ignore it.
Wait for the notebook instance to start, this takes a few minutes.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Create the Notebook instance
Task 2. Load the data
The GitHub repo contains both the lab file and solutions files for the course.
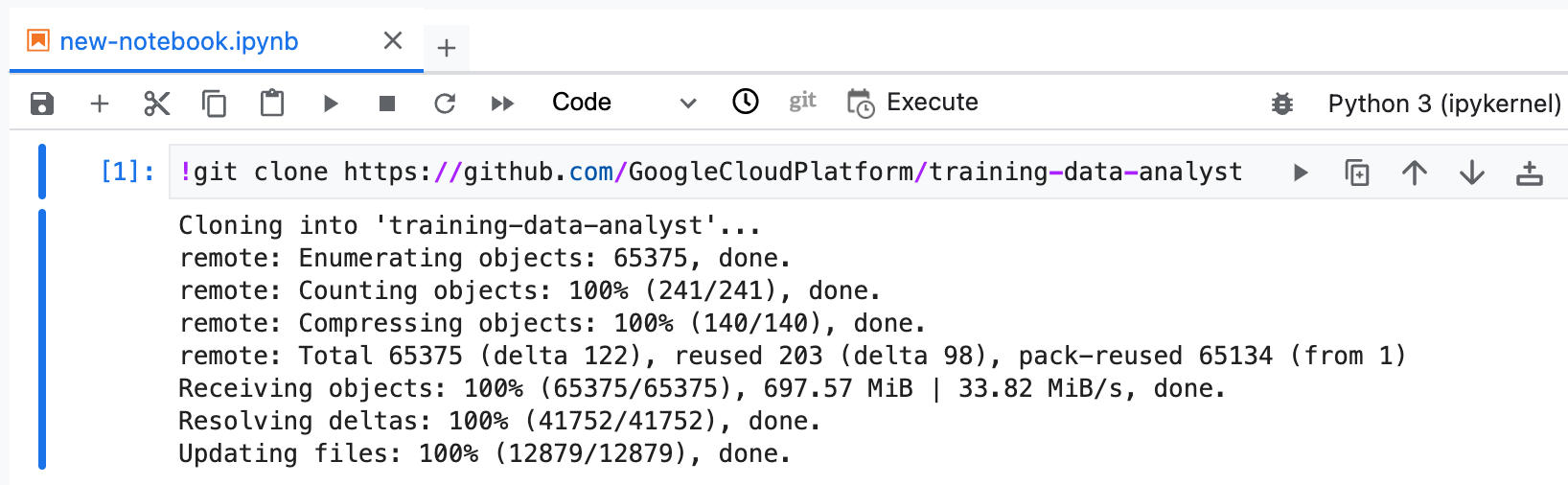
- Copy and run the following code in the first cell of your notebook to clone the
training-data-analyst repository.
!git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/training-data-analyst
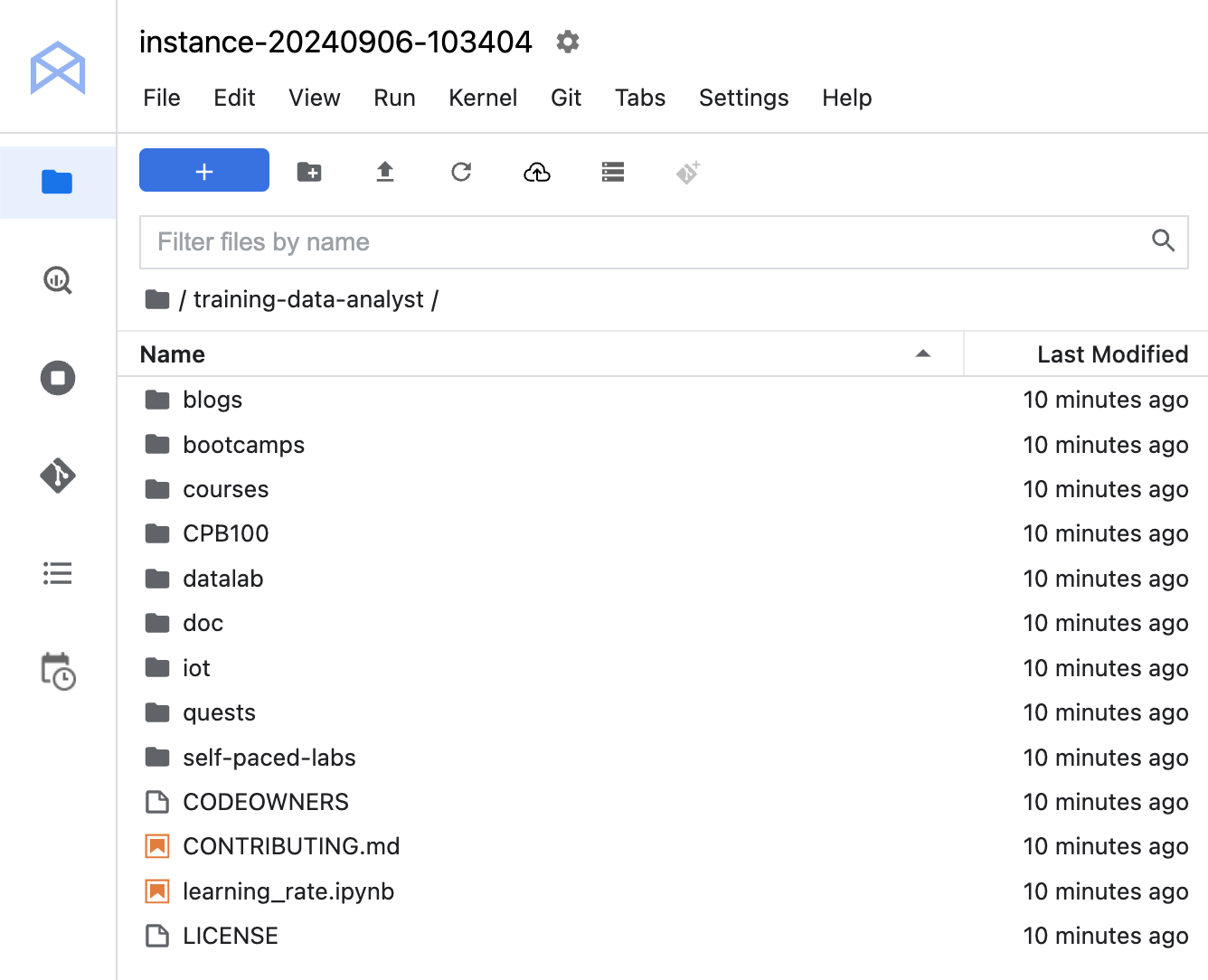
- Confirm that you have cloned the repository. Double-click on the
training-data-analyst directory and ensure that you can see its contents.
Wait for the cloning to complete.
Task 3. Open the notebook
-
Open training-data-analyst > blogs > bitcoin_network > visualizing_the_10000_pizza_bitcoin_network.ipynb.
-
In the notebook interface, click on Edit > Clear All Outputs.
-
Read through the notebook and execute the code to perform the data extraction, cleanup, and visualization.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Load the notebook
Congratulations!
You have seen how you can deploy Vertex AI Workspace notebooks in Google Cloud and retrieve BigQuery data from within a notebook.
Manual Last Updated October 26, 2023
Lab Last Tested October 26, 2022
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.



 , click Vertex AI > Workbench.
, click Vertex AI > Workbench.






