GSP865

Overview
BigQuery is Google's fully managed, NoOps, low cost analytics database. With BigQuery you can query terabytes and terabytes of data without having any infrastructure to manage or needing a database administrator. BigQuery uses SQL and can take advantage of the pay-as-you-go model. BigQuery allows you to focus on analyzing data to find meaningful insights.
In this lab you will ingest subsets of the NYC taxi trips data into tables inside of BigQuery.
What you'll learn
- Loading data into BigQuery from various sources
- Loading data into BigQuery using the CLI and Console
- Using DDL to create tables
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources are made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
Note: Use an Incognito (recommended) or private browser window to run this lab. This prevents conflicts between your personal account and the student account, which may cause extra charges incurred to your personal account.
- Time to complete the lab—remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
Note: Use only the student account for this lab. If you use a different Google Cloud account, you may incur charges to that account.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a dialog opens for you to select your payment method.
On the left is the Lab Details pane with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account.
-
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}}
You can also find the Username in the Lab Details pane.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}}
You can also find the Password in the Lab Details pane.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials.
Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges.
-
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.
Note: To access Google Cloud products and services, click the Navigation menu or type the service or product name in the Search field.

Open the BigQuery console
- In the Google Cloud Console, select Navigation menu > BigQuery.
The Welcome to BigQuery in the Cloud Console message box opens. This message box provides a link to the quickstart guide and the release notes.
- Click Done.
The BigQuery console opens.
Task 1. Create a new dataset to store tables
- In the BigQuery console, click on the View actions icon (
 ) next to your Project ID and click Create dataset.
) next to your Project ID and click Create dataset.
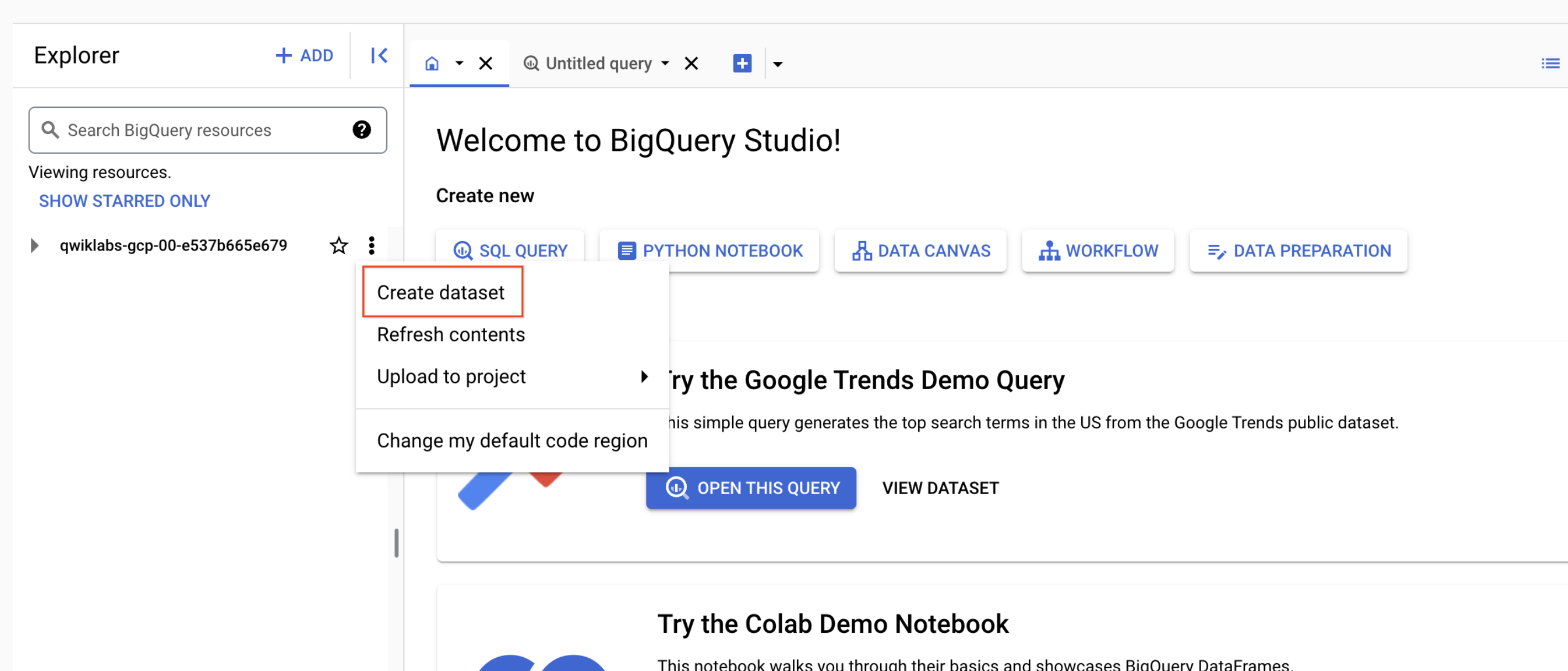
-
Set the Dataset ID to nyctaxi. Leave the other fields at their default values.
-
Click Create dataset.
You'll now see the nyctaxi dataset under your project name.
To check your progress in this lab, click Check my progress below. A checkmark means you're successful.
Creating a dataset to store new tables
Task 2. Ingest a new dataset from a CSV
In this section, you will load a local CSV into a BigQuery table.
-
Download a subset of the NYC taxi 2018 trips data locally onto your computer from this link.
-
In the BigQuery Console, click View actions icon next to nyctaxi dataset then click Create table.
-
Specify the following table options:
Source:
- Create table from: Upload
- Select file: Browse the file you downloaded locally earlier
- File format: CSV
Destination:
Leave all other settings at default.
Schema:
- Check Auto Detect (tip: Not seeing the checkbox? Ensure the file format is CSV and not Avro)
Advanced Options
- Click Create Table.
You should now see the 2018trips table below the nyctaxi dataset.
Select the 2018trips table and view details:
- Select Preview and confirm all columns have been loaded.
You have successfully loaded CSV file into a new BigQuery table.
Run SQL queries
Next, practice with a basic query on the 2018trips table.
- In the Query Editor, write a query to list the top 5 most expensive trips of the year:
#standardSQL
SELECT
*
FROM
nyctaxi.2018trips
ORDER BY
fare_amount DESC
LIMIT 5
To check your progress in this lab, click Check my progress below. A checkmark means you're successful.
Ingest a new dataset from a CSV
Task 3. Ingest a new dataset from Google Cloud Storage
Now, try to load another subset of the same 2018 trip data that is available on Cloud Storage. And this time, let's use the CLI tool to do it.
- In your Cloud Shell, run the following command:
bq load \
--source_format=CSV \
--autodetect \
--noreplace \
nyctaxi.2018trips \
gs://spls/gsp865/OCBL013/nyc_tlc_yellow_trips_2018_subset_2.csv
Note: With the above load job, you are specifying that this subset is to be appended to the existing 2018trips table that you created above.
When the load job is complete, you will get a confirmation on the screen.
-
Back on your BigQuery console, select the 2018trips table and view details. Confirm that the row count has now almost doubled.
-
You may want to run the earlier query to see if the top 5 most expensive trips have changed.
To check your progress in this lab, click Check my progress below. A checkmark means you're successful.
Ingest a dataset from Google Cloud Storage
Task 4. Create tables from other tables with DDL
The 2018trips table now has trips from throughout the year. What if you were only interested in January trips? For the purpose of this lab, we will keep it simple and focus only on pickup date and time. Let's use DDL to extract this data and store it in another table
- In the Query Editor, run the following
CREATE TABLE command :
#standardSQL
CREATE TABLE
nyctaxi.january_trips AS
SELECT
*
FROM
nyctaxi.2018trips
WHERE
EXTRACT(Month
FROM
pickup_datetime)=1;
- Now run the below query in your Query Editor find the longest distance traveled in the month of January:
#standardSQL
SELECT
*
FROM
nyctaxi.january_trips
ORDER BY
trip_distance DESC
LIMIT
1
To check your progress in this lab, click Check my progress below. A checkmark means you're successful.
Create tables from other tables with DDL
Congratulations!
You've successfully created a new dataset and ingested data into BigQuery from CSV, Google Cloud Storage, and other BigQuery tables.
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated: August 21, 2025
Lab Last Tested: November 05, 2024
Copyright 2025 Google LLC. All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.



 ) next to your Project ID and click Create dataset.
) next to your Project ID and click Create dataset.





