
始める前に
- ラボでは、Google Cloud プロジェクトとリソースを一定の時間利用します
- ラボには時間制限があり、一時停止機能はありません。ラボを終了した場合は、最初からやり直す必要があります。
- 画面左上の [ラボを開始] をクリックして開始します
Install trident
/ 10
Create secret
/ 10
Create backend
/ 10
Create storage class
/ 10
Create a volume
/ 10
This lab was developed with our partner, NetApp. Your personal information may be shared with NetApp, the lab sponsor, if you have opted-in to receive product updates, announcements, and offers in your Account Profile.
Netapp Trident enables consumption and management of storage resources across all popular NetApp storage platforms, including Google Cloud NetApp Volumes. Trident is a Container Storage Interface (CSI) compliant dynamic storage orchestrator that natively integrates with Kubernetes. Trident runs as a single Controller Pod plus a Node Pod on each worker node in the cluster.
In this lab you will learn how to create persistent volumes in Google Kubernetes Engine using Google Cloud NetApp Volumes.
In this lab you will learn how to:
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This Qwiklabs hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Note: If you already have your own personal Google Cloud account or project, do not use it for this lab.
Note: If you are using a Pixelbook, open an Incognito window to run this lab.
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is a panel populated with the temporary credentials that you must use for this lab.
Copy the username, and then click Open Google Console. The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Open the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
In the Sign in page, paste the username that you copied from the Connection Details panel. Then copy and paste the password.
Important: You must use the credentials from the Connection Details panel. Do not use your Qwiklabs credentials. If you have your own Google Cloud account, do not use it for this lab (avoids incurring charges).
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Cloud Console opens in this tab.
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
In the Cloud Console, in the top right toolbar, click the Activate Cloud Shell button.
Click Continue.
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID. For example:
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
You can list the active account name with this command:
(Output)
(Example output)
You can list the project ID with this command:
(Output)
(Example output)
Open the Kubernetes Engine console and verify that there is an existing kubernetes cluster running.
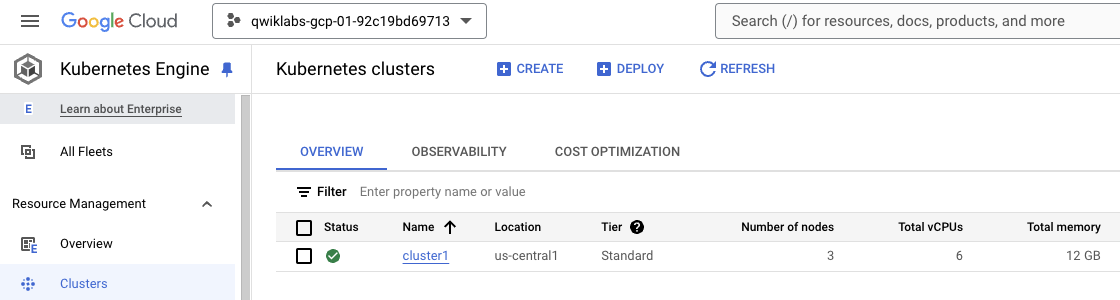
Open a Google Cloud Shell and run the below command to connect to the kubernetes cluster.
You can verify that you have connected properly running the next command.
First, download a copy of Trident to your local computer that has kubectl installed and has kubectl access to your Kubernetes cluster.
Be sure to unzip the file after download and go to the directory.
Next, install the custom resource definition (CRD) for the Trident orchestrator custom resource (CR). The YAML file for the CRD is included in the bundle you just downloaded.
Next, create the trident namespace and deploy the operator along with the service account and role-based access control (RBAC) for the operator.
You should now see the operator appear in your cluster.
Wait until the trident operator pod is running like the below example.
Deploy the Trident orchestrator CR.
This resource will deploy several pods: a controller pod and a pod on each worker node.
Wait until the trident controller pods are running like the below example.
Click Check my progress to verify that you've performed the above task.
And attach the netapp admin permissions to the new service account.
Go to the IAM & Admin console, and click on the Service Accounts section. Click on the service account 'netapp-trident' that you has just created, click on the KEYS tab, and click on ADD KEY > Create new key. Select the JSON format to download it.
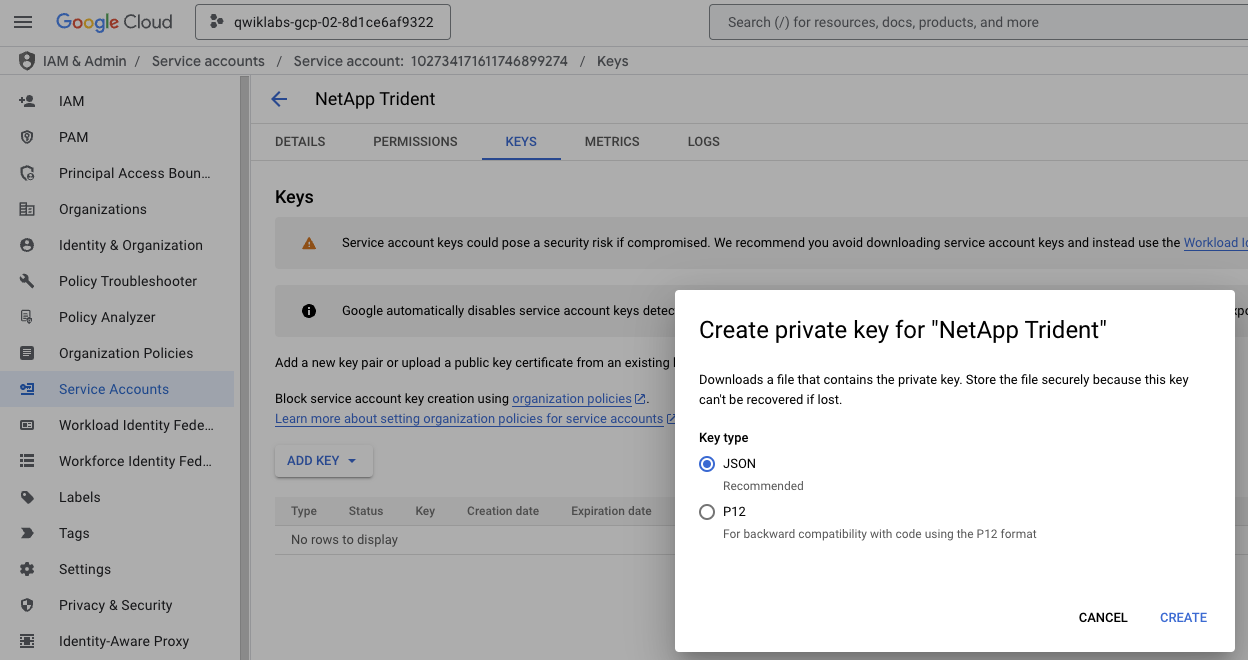
A secret is an object that contains a small amount of sensitive data such as a password, a token, or a key.
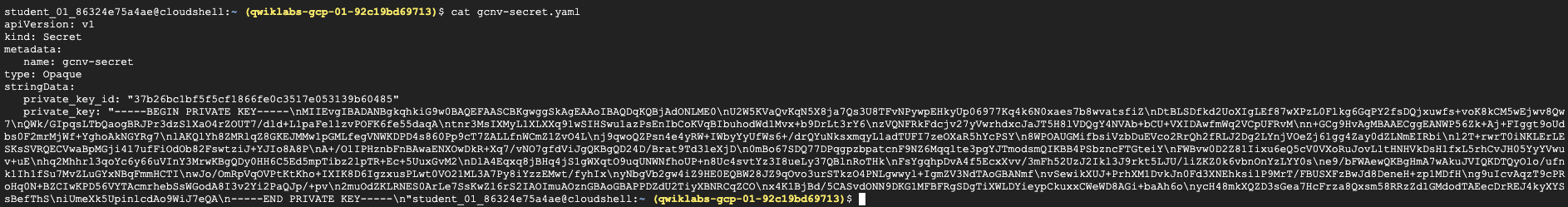
Create a new file gcnv-secret.yaml in the Cloud Shell, copy the below yaml file and include the private_key_id and private_key replacing the '<-- Include here -->' text with the values of the service account json file.
The gcnv-secret.yaml file should look similar to the below one.
Create and verify the Kubernetes secret using the next commands.
Click Check my progress to verify that you've performed the above task.
A backend defines the relationship between Trident and a storage system. It tells Trident how to communicate with that storage system and how Trident should provision volumes from it.
Get and copy the project number running the next command from the Cloud Shell.
Create a new file gcnv-backend-zonal-flex.yaml in the Cloud Shell, copy the below yaml file and include the client_id replacing the '<-- Include here -->' text with the value of the service account json file, and include the project number replacing the '<-- Include here -->' text that you just got in the previous step.
Create and verify the Kubernetes backend using the next commands.
Click Check my progress to verify that you've performed the above task.
A Kuberetes StorageClass provides a way for administrators to describe the classes of storage they offer. Different classes might map to quality-of-service levels, or to backup policies, or to arbitrary policies determined by the cluster administrators.
Create a new file gcnv-storageclass-zonal-flex.yaml in the Cloud Shell, copy the below yaml file.
Create and verify the Kubernetes Storage Class using the next commands.
Click Check my progress to verify that you've performed the above task.
A Persistent Volume (PV) is a physical storage resource provisioned by the cluster administrator on a Kubernetes cluster. The Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) is a request for access to the Persistent Volume on the cluster.
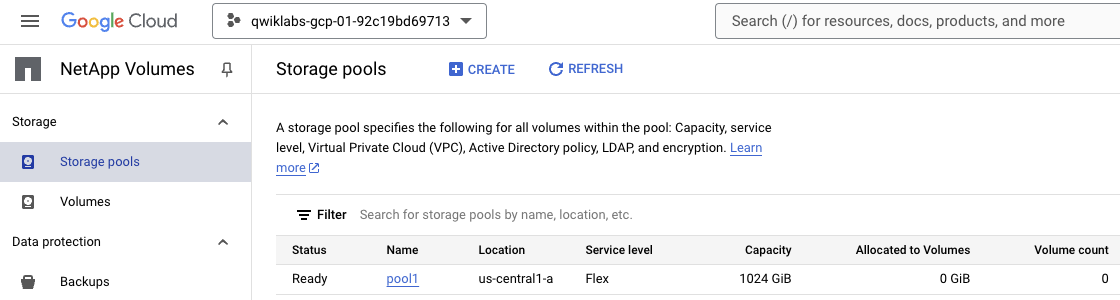
Open the NetApp Volumes console and verify that there is a existing Storage Pool running.
Create a new file gcnv-pvc-zonal-flex.yaml in the Cloud Shell, copy the below yaml file.
Create and verify the Kubernetes Persistent Volume Claim using the next commands.
Open the Google Cloud NetApp Volumes console and verify that there is a new volume created similar like the below.
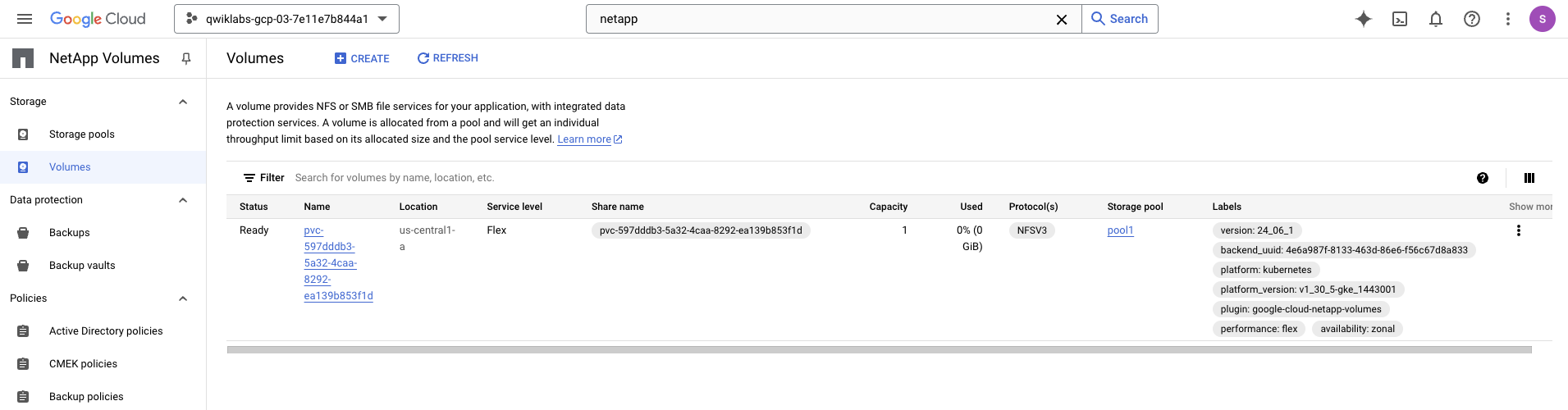
Verify the Kubernetes Persistent Volume using the next command.
Click Check my progress to verify that you've performed the above task.
You have learned how to create a Kuberentes persistent volume dynamically with Google Cloud NetApp Volumes from Google Kubernetes Engine using NetApp Trident.
Be sure to check out the official NetApp Volumes documentation:
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual last updated April 15, 2025
Manual Last tested April 15, 2025
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




このコンテンツは現在ご利用いただけません
利用可能になりましたら、メールでお知らせいたします

ありがとうございます。
利用可能になりましたら、メールでご連絡いたします


1 回に 1 つのラボ
既存のラボをすべて終了して、このラボを開始することを確認してください
