
始める前に
- ラボでは、Google Cloud プロジェクトとリソースを一定の時間利用します
- ラボには時間制限があり、一時停止機能はありません。ラボを終了した場合は、最初からやり直す必要があります。
- 画面左上の [ラボを開始] をクリックして開始します
Create Compute Engine VMs
/ 10
Enable APIs
/ 10
Discover the Datadog provider
/ 10
Create a simple workflow
/ 10
Create an Eventarc trigger
/ 10
Test Datadog monitor and trigger execution
/ 10
Enable Datadog's Google Cloud integration
/ 10
Create a workflow
/ 10
Create an Eventarc trigger for Compute
/ 10
Test Datadog monitor and trigger
/ 10
This lab was developed with our partner, Datadog. Your personal information may be shared with Datadog, the lab sponsor, if you have opted-in to receive product updates, announcements, and offers in your Account Profile.
Eventarc makes it easy to connect Google Cloud services with events from a variety of sources. It allows you to build event-driven architectures in which microservices are loosely coupled and distributed. It also takes care of event ingestion, delivery, security, authorization, and error-handling for you which improves developer agility and application resilience.
Datadog is a monitoring and security platform for cloud applications. It brings together end-to-end traces, metrics, and logs to make your applications, infrastructure, and third-party services observable.
In this lab you will learn about using the Helm chart used to install the Datadog Agent. You will learn to:
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This Qwiklabs hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
Note: If you already have your own personal Google Cloud account or project, do not use it for this lab.
Note: If you are using a Pixelbook, open an Incognito window to run this lab.
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is a panel populated with the temporary credentials that you must use for this lab.
Copy the username, and then click Open Google Console. The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Open the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
In the Sign in page, paste the username that you copied from the Connection Details panel. Then copy and paste the password.
Important: You must use the credentials from the Connection Details panel. Do not use your Qwiklabs credentials. If you have your own Google Cloud account, do not use it for this lab (avoids incurring charges).
Click through the subsequent pages:
After a few moments, the Cloud Console opens in this tab.
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
In the Cloud Console, in the top right toolbar, click the Activate Cloud Shell button.
Click Continue.
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID. For example:
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
You can list the active account name with this command:
(Output)
(Example output)
You can list the project ID with this command:
(Output)
(Example output)
PROJECT_ID variable.Also, set a REGION variable to the default region as described below. This is the region you will create resources in later.
You will start with some Compute Engine Virtual Machines (VMs). You will not be using them right away. Later in the lab you will use Datadog Google Cloud integration to monitor these VMs.
You should see VMs created and running in a minute or so in the Cloud Console.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
If you already have a trial account set up, you can use that. It is recommended that you do not use your production Datadog account to avoid cluttering the environment with test and training assets.
Navigate to https://us5.datadoghq.com/signup and enter your name, email, company, and a password. Make sure United States (US5-Central) is selected.
On the next page, close the Datadog sign up workflow by clicking on the Datadog icon.
An Eventarc provider is a service or entity that can emit events directly to Google Cloud which are then routed to your project. Third-party providers, such as Datadog, are non-Google Cloud providers that are integrated with Google Cloud through Eventarc.
This lists Google Cloud and third-party providers and the locations they are available in:
You can narrow down the list to third-party providers with this command:
You should see Datadog in the list:
You can also describe the Datadog provider to see the events it supports:
You need to set up a channel to integrate your project with a provider. This involves creating a channel, retrieving channel details and sending those details to the provider. Once the provider has initialized the connection to the channel, the provider can start sending events to your project.
You can do it using gcloud:
Or create it from the Channels section of the Eventarc page in Google Cloud Console:
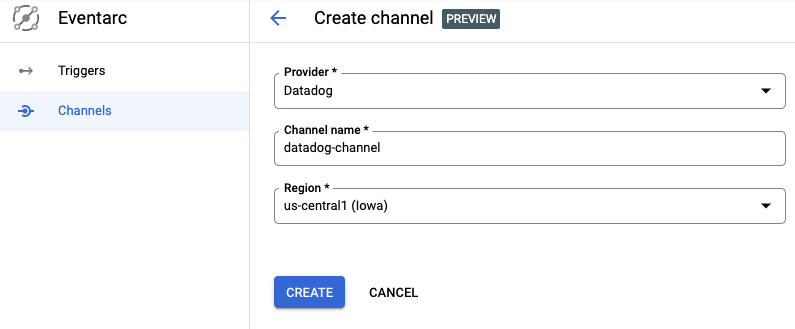
gcloud:The output should be similar to the following:
Similarly, you can see the channel from Google Cloud Console:
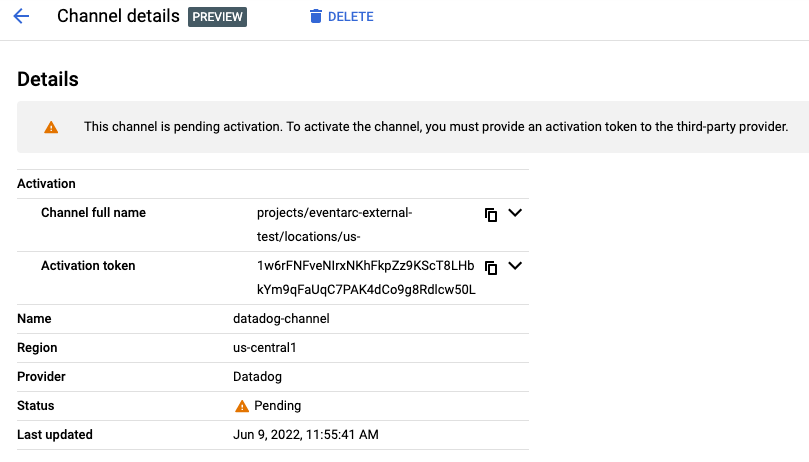
The channel state indicates the channel's status. It can be one of the following:
PENDING—The channel has been created successfully and there is an activation token available to create a connection with the provider. To change the state of the channel from PENDING to ACTIVE, the token must be given to the provider and used to connect the channel within 24 hours of the channel's creation.ACTIVE—The channel has been successfully connected with the provider. An ACTIVE channel is ready to receive and route events from the provider.INACTIVE—The channel cannot receive events nor be reactivated. The provider is either disconnected from this channel or the channel activation token has expired and the provider isn't connected. To re-establish a connection with a provider, you must create a new channel for the provider.An activation token is a single-use, time-restricted token, used to create a connection between a provider and a subscriber's project. Only a specific provider, selected during the channel creation process can use the token. The token is valid for 24 hours after the channel's creation. After 24 hours, the channel becomes INACTIVE.
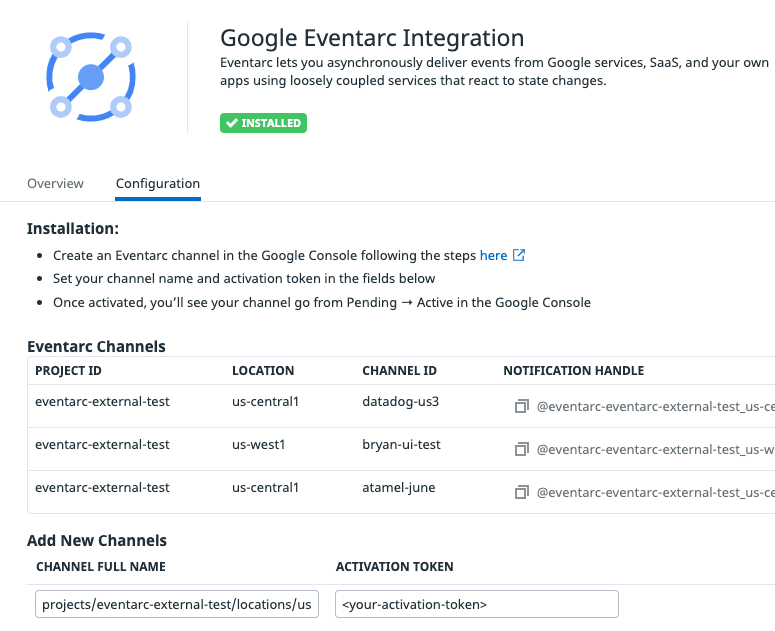
You need to send the following channel details to the Datadog provider:
projects/qwiklabs-gcp-04-4e022c25f345/locations/us-east1/channels/datadog-channel)so5g4Kdasda7y2MSasdaGn8njB2)Integrations page and search for Google Eventarc. Click the Configure button. If it is not installed, click on the Install button.
You should now see the channel in the list of channels and after a few seconds, you should also see the channel become active in Google Cloud Console:
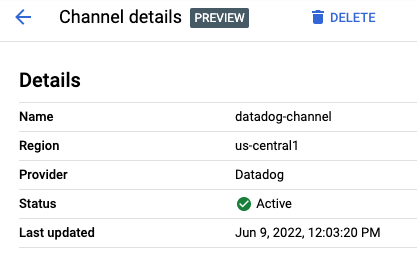
Now, you're ready to use the channel!
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You need a destination in Google Cloud to receive events from the provider. Eventarc supports a number of event destinations such as Cloud Run, Workflows, Kubernetes services. In this case, deploy a workflow to simply log the received events.
workflow-datadog1.yaml:Note that the workflow is receiving an event as a parameter. This event will come from Datadog monitoring via Eventarc. Once the event is received, the workflow simply logs the received event.
The workflow is deployed but it's not running yet. It will be executed by an Eventarc trigger when a Datadog alert is received.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You are now ready to connect events from the Datadog provider to Workflows with an Eventarc trigger.
You need a service account with the eventarc.eventReceiver role when creating a trigger. You can either create a dedicated service account or use the default compute service account.
eventarc.eventReceiver role:The output will look like this:
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You will now create a Datadog monitor and connect it to Eventarc.
It will be a Hello World type monitor with default values. You will manually trigger it to generate the monitoring alerts which in turn will generate an Eventarc event in Google Cloud.
To create a monitor in Datadog, log in to Datadog. Hover over Monitors in the main menu and click New Monitor in the sub-menu. There are many monitor types. Choose the Metric monitor type.
In the New Monitor page, leave the defaults for steps 1 and 2.
In step 3, set Alert threshold to 1
In step 4, set Test monitor for Eventarc as the monitor name and click @ Add Mention to select @eventarc_
Keep the monitor page open for the next step where you will test the monitor.
To test the Datadog monitor and the Eventarc trigger, you will manually trigger the monitor.
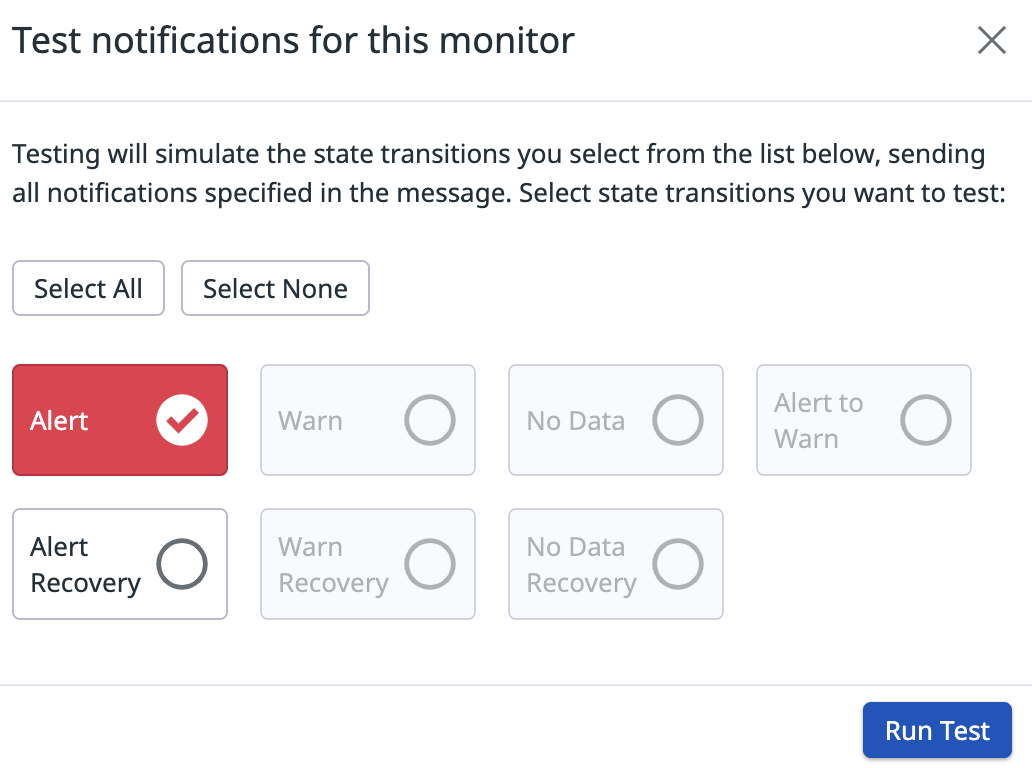
This should simulate the state transition in the monitor and trigger an Eventarc event.
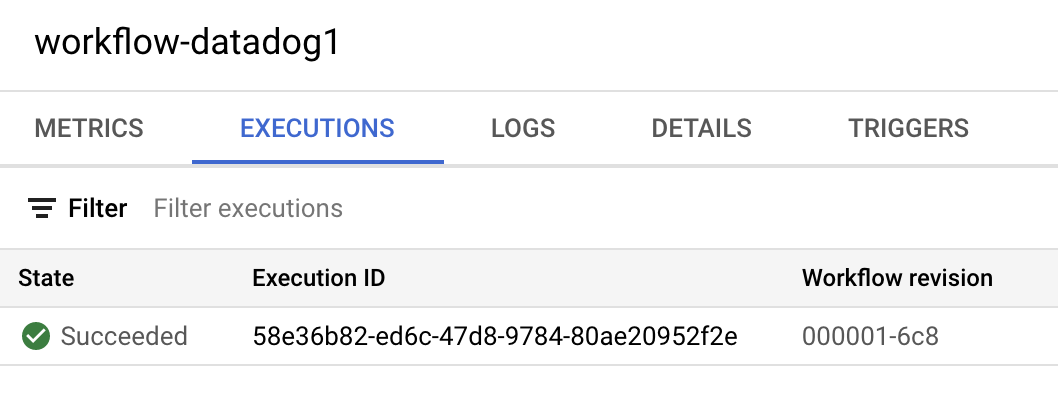
datadog.v1.alert generated from the monitoring alert in the input of the workflow and also in the logs: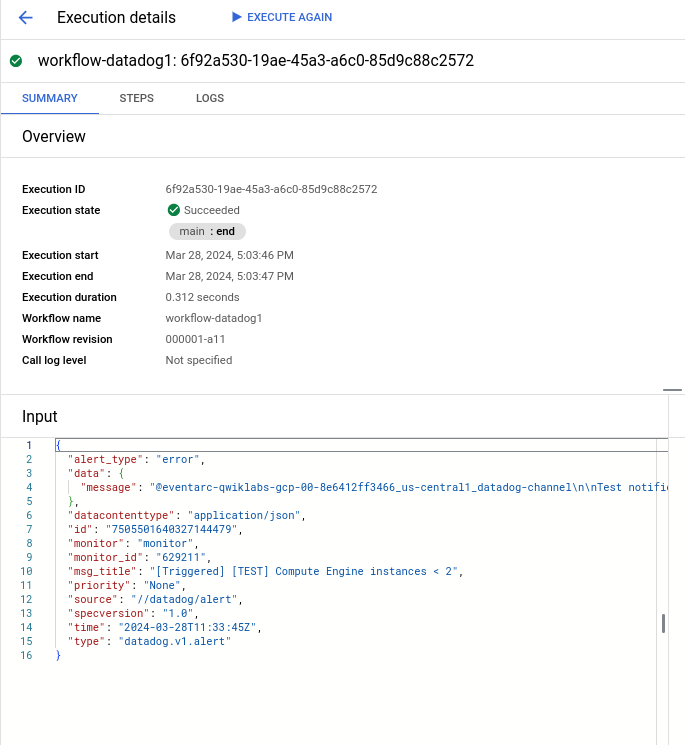
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
To use Datadog to monitor a project, you need to enable APIs needed for Datadog, create a service account, and connect the service account to Datadog.
Datadog's Google Cloud integration uses a service account to make calls to the Cloud Logging API to collect node-level metrics from your Compute Engine instances.
In Datadog, navigate to Integrations, search for Google Cloud Platform and select it.
Click on Add GCP Account. If you have no configured projects, you are automatically redirected to this page.
If you have not generated a Datadog principal for your org, click the Generate Principal button.
Copy your Datadog principal to the clipboard and keep it for the next section.
Back in the Google Cloud console, under the IAM & Admin > Service Acounts menu, find the service account you created in the first section.
Go to the Permissions tab and click on Grant Access.
Paste your Datadog principal into the New principals text box.
Assign the role of Service Account Token Creator and click Save.
In your Google Cloud console, navigate to the Service Account > Details tab for the service account you created. There, you can find the email associated with this Google service account. It resembles <sa-name>@<project-id>.iam.gserviceaccount.com. Copy this email.
Return to the integration configuration tile in Datadog (where you copied your Datadog principal in the previous section).
In the box under Add Service Account Email, paste the email you previously copied.
Click on Verify and Save Account.
Now that you have 2 VMs running, create a workflow that will respond to alerts from a Datadog monitor. The workflow can be as sophisticated as you like but in this case, the workflow will check the number of VM instances running and if it falls below 2, it will create new VM instances to make sure there are 2 VMs running at all times.
workflow-datadog2.yaml file:Note that the workflow is receiving an event as a parameter. This event will come from Datadog monitoring via Eventarc. Once the event is received, the workflow checks the number of running instances and creates new VM instances, if needed.
The workflow is deployed but it's not running yet. It will be executed by an Eventarc trigger when a Datadog alert is received.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You are now ready to connect events from the Datadog provider to Workflows with an Eventarc trigger. You will use the channel and the service account you set up in the first codelab.
You can list the triggers to see that the newly created trigger is active:
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
You will now create a Datadog monitor and connect it to Eventarc.
The monitor will check the number of Compute Engine VMs running and alert if it falls below 2.
To create a monitor in Datadog, log in to Datadog. Hover over Monitors in the main menu and click New Monitor in the sub-menu. There are many monitor types. Choose the Metric monitor type.
In the New Monitor page, create a monitor with the following:
Choose the detection method: Threshold Alert.
Define the metric: gcp.gce.instance.is_running from (everywhere) sum by (everything)
Evaluate the minimum of the query over the last 5 minutes
Set alert conditions:
below the threshold< 2
Notify your team:
Compute Engine instances < 2
Create at the bottom to create the monitor.After a few seconds, you should see the instance deleted in Google Cloud Console.
There's a bit of latency for this change to show up in Datadog. After some time (typically 10 mins), you should see the monitor in Datadog to detect and alert this under Manage Monitors section:
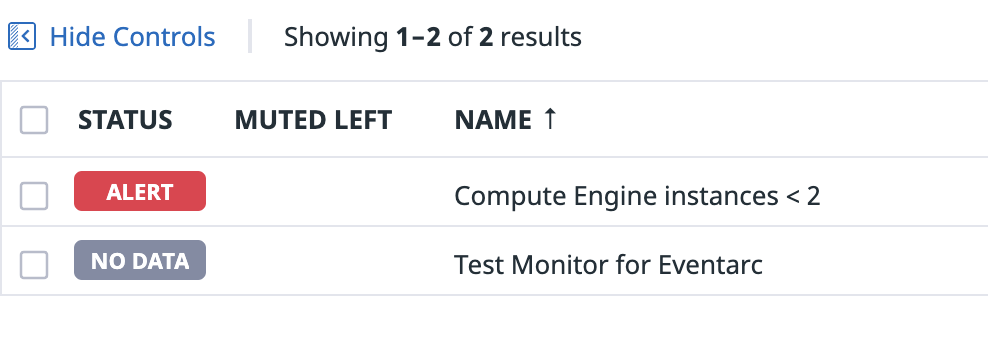
Once the Datadog monitor alerts, you should see that alert go to Workflows via Eventarc. If you check the logs of Workflows, you should see that Workflows checks to find out the difference between the current instance count and expected instance count:
2022-09-28 09:30:53.371 BST instanceCount->1 diffInstanceCount->1
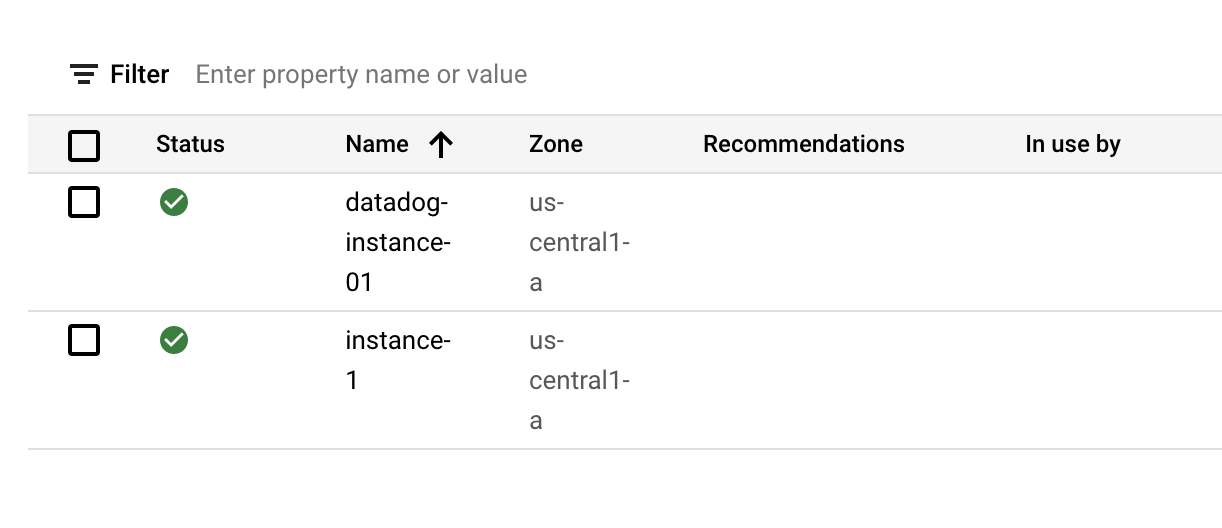
It responds to that alert by creating a new VM instance with datadog-instance-## prefix.
In the end, you will still have 2 VMs in your project, one you created initially and the other one created by Workflows after the Datadog alert!
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
In this lab you got hands-on experience using the Datadog Monitors and Google Eventarc.
Be sure to check out the following labs for more practice with Datadog:
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.




このコンテンツは現在ご利用いただけません
利用可能になりましたら、メールでお知らせいたします

ありがとうございます。
利用可能になりましたら、メールでご連絡いたします


1 回に 1 つのラボ
既存のラボをすべて終了して、このラボを開始することを確認してください
